Page 76 - Read Online
P. 76
Gharagozloo et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:66 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.53 Page 17 of 22
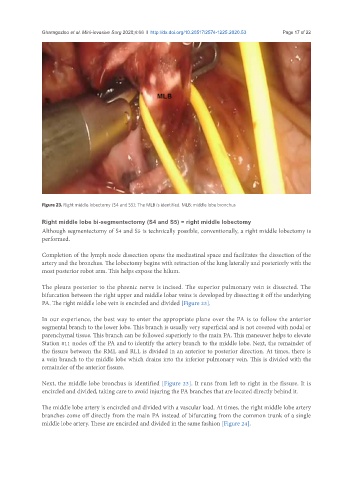
Figure 23. Right middle lobectomy (S4 and S5): The MLB is identified. MLB: middle lobe bronchus
Right middle lobe bi-segmentectomy (S4 and S5) = right middle lobectomy
Although segmentectomy of S4 and S5 is technically possible, conventionally, a right middle lobectomy is
performed.
Completion of the lymph node dissection opens the mediastinal space and facilitates the dissection of the
artery and the bronchus. The lobectomy begins with retraction of the lung laterally and posteriorly with the
most posterior robot arm. This helps expose the hilum.
The pleura posterior to the phrenic nerve is incised. The superior pulmonary vein is dissected. The
bifurcation between the right upper and middle lobar veins is developed by dissecting it off the underlying
PA. The right middle lobe vein is encircled and divided [Figure 23].
In our experience, the best way to enter the appropriate plane over the PA is to follow the anterior
segmental branch to the lower lobe. This branch is usually very superficial and is not covered with nodal or
parenchymal tissue. This branch can be followed superiorly to the main PA. This maneuver helps to elevate
Station #11 nodes off the PA and to identify the artery branch to the middle lobe. Next, the remainder of
the fissure between the RML and RLL is divided in an anterior to posterior direction. At times, there is
a vein branch to the middle lobe which drains into the inferior pulmonary vein. This is divided with the
remainder of the anterior fissure.
Next, the middle lobe bronchus is identified [Figure 23]. It runs from left to right in the fissure. It is
encircled and divided, taking care to avoid injuring the PA branches that are located directly behind it.
The middle lobe artery is encircled and divided with a vascular load. At times, the right middle lobe artery
branches come off directly from the main PA instead of bifurcating from the common trunk of a single
middle lobe artery. These are encircled and divided in the same fashion [Figure 24].