Page 77 - Read Online
P. 77
Page 18 of 22 Gharagozloo et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:66 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.53
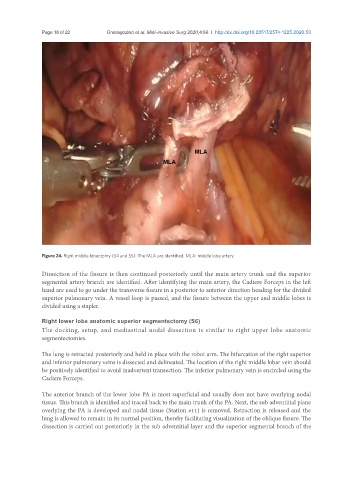
Figure 24. Right middle lobectomy (S4 and S5): The MLA are identified. MLA: middle lobe artery
Dissection of the fissure is then continued posteriorly until the main artery trunk and the superior
segmental artery branch are identified. After identifying the main artery, the Cadiere Forceps in the left
hand are used to go under the transverse fissure in a posterior to anterior direction heading for the divided
superior pulmonary vein. A vessel loop is passed, and the fissure between the upper and middle lobes is
divided using a stapler.
Right lower lobe anatomic superior segmentectomy (S6)
The docking, setup, and mediastinal nodal dissection is similar to right upper lobe anatomic
segmentectomies.
The lung is retracted posteriorly and held in place with the robot arm. The bifurcation of the right superior
and inferior pulmonary veins is dissected and delineated. The location of the right middle lobar vein should
be positively identified to avoid inadvertent transection. The inferior pulmonary vein is encircled using the
Cadiere Forceps.
The anterior branch of the lower lobe PA is most superficial and usually does not have overlying nodal
tissue. This branch is identified and traced back to the main trunk of the PA. Next, the sub adventitial plane
overlying the PA is developed and nodal tissue (Station #11) is removed. Retraction is released and the
lung is allowed to remain in its normal position, thereby facilitating visualization of the oblique fissure. The
dissection is carried out posteriorly in the sub adventitial layer and the superior segmental branch of the