Page 12 - Read Online
P. 12
Kobayashi et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:30 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.12 Page 7 of 8
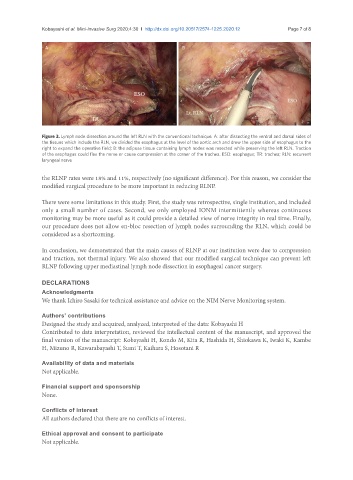
A B
Figure 3. Lymph node dissection around the left RLN with the conventional technique. A: after dissecting the ventral and dorsal sides of
the tissues which include the RLN, we divided the esophagus at the level of the aortic arch and drew the upper side of esophagus to the
right to expand the operative field; B: the adipose tissue containing lymph nodes was resected while preserving the left RLN. Traction
of the esophagus could flex the nerve or cause compression at the corner of the trachea. ESO: esophagus; TR: trachea; RLN: recurrent
laryngeal nerve
the RLNP rates were 18% and 11%, respectively (no significant difference). For this reason, we consider the
modified surgical procedure to be more important in reducing RLNP.
There were some limitations in this study. First, the study was retrospective, single institution, and included
only a small number of cases. Second, we only employed IONM intermittently whereas continuous
monitoring may be more useful as it could provide a detailed view of nerve integrity in real time. Finally,
our procedure does not allow en-bloc resection of lymph nodes surrounding the RLN, which could be
considered as a shortcoming.
In conclusion, we demonstrated that the main causes of RLNP at our institution were due to compression
and traction, not thermal injury. We also showed that our modified surgical technique can prevent left
RLNP following upper mediastinal lymph node dissection in esophageal cancer surgery.
DECLARATIONS
Acknowledgments
We thank Ichiro Sasaki for technical assistance and advice on the NIM Nerve Monitoring system.
Authors’ contributions
Designed the study and acquired, analyzed, interpreted of the data: Kobayashi H
Contributed to data interpretation, reviewed the intellectual content of the manuscript, and approved the
final version of the manuscript: Kobayashi H, Kondo M, Kita R, Hashida H, Shiokawa K, Iwaki K, Kambe
H, Mizuno R, Kawarabayashi T, Sumi T, Kaihara S, Hosotani R
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Financial support and sponsorship
None.
Conflicts of interest
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.