Page 39 - Read Online
P. 39
Page 8 of 12 Tschuor et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:72 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.39
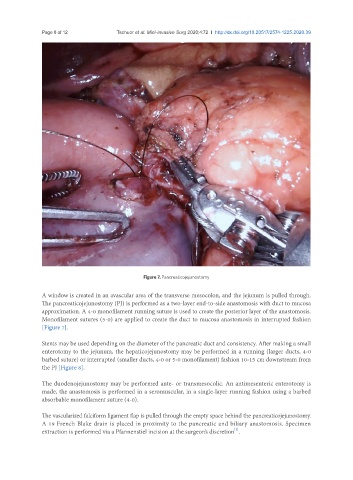
Figure 7. Pancreaticojejunostomy
A window is created in an avascular area of the transverse mesocolon, and the jejunum is pulled through.
The pancreaticojejunostomy (PJ) is performed as a two-layer end-to-side anastomosis with duct to mucosa
approximation. A 4-0 monofilament running suture is used to create the posterior layer of the anastomosis.
Monofilament sutures (5-0) are applied to create the duct to mucosa anastomosis in interrupted fashion
[Figure 7].
Stents may be used depending on the diameter of the pancreatic duct and consistency. After making a small
enterotomy to the jejunum, the hepaticojejunostomy may be performed in a running (larger ducts, 4-0
barbed suture) or interrupted (smaller ducts, 4-0 or 5-0 monofilament) fashion 10-15 cm downstream from
the PJ [Figure 8].
The duodenojejunostomy may be performed ante- or transmesocolic. An antimesenteric enterotomy is
made, the anastomosis is performed in a seromuscular, in a single-layer running fashion using a barbed
absorbable monofilament suture (4-0).
The vascularized falciform ligament flap is pulled through the empty space behind the pancreaticojejunostomy.
A 19 French Blake drain is placed in proximity to the pancreatic and biliary anastomosis. Specimen
[2]
extraction is performed via a Pfannenstiel incision at the surgeon’s discretion .