Page 36 - Read Online
P. 36
Tschuor et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:72 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2020.39 Page 5 of 12
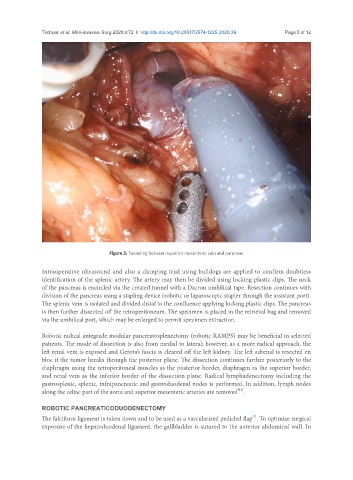
Figure 3. Tunneling between superior mesenteric vein and pancreas
Intraoperative ultrasound and also a clamping trial using bulldogs are applied to confirm doubtless
identification of the splenic artery. The artery may then be divided using locking plastic clips. The neck
of the pancreas is encircled via the created tunnel with a Dacron umbilical tape. Resection continues with
division of the pancreas using a stapling device (robotic or laparoscopic stapler through the assistant port).
The splenic vein is isolated and divided distal to the confluence applying locking plastic clips. The pancreas
is then further dissected off the retroperitoneum. The specimen is placed in the retrieval bag and removed
via the umbilical port, which may be enlarged to permit specimen extraction.
Robotic radical antegrade modular pancreatosplenectomy (robotic RAMPS) may be beneficial in selected
patients. The mode of dissection is also from medial to lateral; however, as a more radical approach, the
left renal vein is exposed and Gerota’s fascia is cleared off the left kidney. The left adrenal is resected en
bloc if the tumor breaks through the posterior plane. The dissection continues further posteriorly to the
diaphragm using the retroperitoneal muscles as the posterior border, diaphragm as the superior border,
and renal vein as the inferior border of the dissection plane. Radical lymphadenectomy including the
gastrosplenic, splenic, infrapancreatic and gastroduodenal nodes is performed. In addition, lymph nodes
[11]
along the celiac part of the aorta and superior mesenteric arteries are removed .
ROBOTIC PANCREATICODUODENECTOMY
[3]
The falciform ligament is taken down and to be used as a vascularized pedicled flap . To optimize surgical
exposure of the hepatoduodenal ligament, the gallbladder is sutured to the anterior abdominal wall. In