Page 59 - Read Online
P. 59
Page 4 of 10 Gharagozloo. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:14 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2019.55
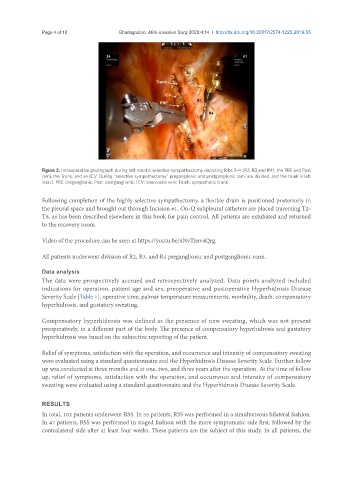
Figure 2. Intraoperative photograph during left robotic selective sympathectomy depicting Ribs 2-4 (R2, R3,and R4), the PRE and Post
rami, the Trunk, and an ICV. During “selective sympathectomy” preganglionic and postganglionic rami are divided, and the trunk is left
intact. PRE: preganglionic; Post: postganglionic; ICV: intercostal vein; Trunk: sympathetic trunk
Following completion of the highly selective sympathectomy, a flexible drain is positioned posteriorly in
the pleural space and brought out through Incision #1. On-Q subpleural catheters are placed traversing T2-
T8, as has been described elsewhere in this book for pain control. All patients are extubated and returned
to the recovery room.
Video of the procedure can be seen at https://youtu.be/8NvTznv4Qrg.
All patients underwent division of R2, R3, and R4 preganglionic and postganglionic rami.
Data analysis
The data were prospectively accrued and retrospectively analyzed. Data points analyzed included
indications for operation, patient age and sex, preoperative and postoperative Hyperhidrosis Disease
Severity Scale [Table 1], operative time, palmar temperature measurements, morbidity, death, compensatory
hyperhidrosis, and gustatory sweating.
Compensatory hyperhidrosis was defined as the presence of new sweating, which was not present
preoperatively, in a different part of the body. The presence of compensatory hyperhidrosis and gustatory
hyperhidrosis was based on the subjective reporting of the patient.
Relief of symptoms, satisfaction with the operation, and occurrence and intensity of compensatory sweating
were evaluated using a standard questionnaire and the Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale. Further follow
up was conducted at three months and at one, two, and three years after the operation. At the time of follow
up, relief of symptoms, satisfaction with the operation, and occurrence and intensity of compensatory
sweating were evaluated using a standard questionnaire and the Hyperhidrosis Disease Severity Scale.
RESULTS
In total, 102 patients underwent RSS. In 55 patients, RSS was performed in a simultaneous bilateral fashion.
In 47 patients, RSS was performed in staged fashion with the more symptomatic side first, followed by the
contralateral side after at least four weeks. These patients are the subject of this study. In all patients, the