Page 62 - Read Online
P. 62
Gharagozloo. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:14 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2019.55 Page 7 of 10
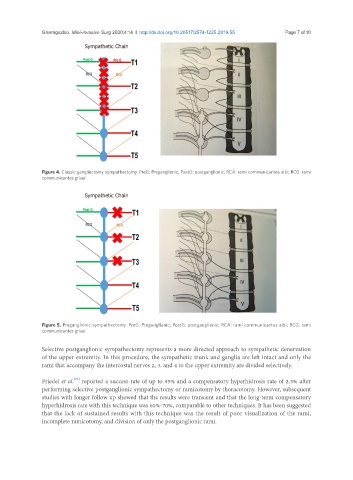
Sympathetic Chain
Figure 4. Classic gangliectomy sympathectomy. PreG: Preganglionic; PostG: postganglionic; RCA: rami communicantes albi; RCG: rami
communicantes grisei
Sympathetic Chain
Figure 5. Preganglionic sympathectomy. PreG: Preganglionic; PostG: postganglionic; RCA: rami communicantes albi; RCG: rami
communicantes grisei
Selective postganglionic sympathectomy represents a more directed approach to sympathetic denervation
of the upper extremity. In this procedure, the sympathetic trunk and ganglia are left intact and only the
rami that accompany the intercostal nerves 2, 3, and 4 to the upper extremity are divided selectively.
[23]
Friedel et al. reported a success rate of up to 95% and a compensatory hyperhidrosis rate of 2.5% after
performing selective postganglionic sympathectomy or ramicotomy by thoracotomy. However, subsequent
studies with longer follow up showed that the results were transient and that the long-term compensatory
hyperhidrosis rate with this technique was 60%-70%, comparable to other techniques. It has been suggested
that the lack of sustained results with this technique was the result of poor visualization of the rami,
incomplete ramicotomy, and division of only the postganglionic rami.