Page 58 - Read Online
P. 58
Gharagozloo. Mini-invasive Surg 2020;4:14 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2019.55 Page 3 of 10
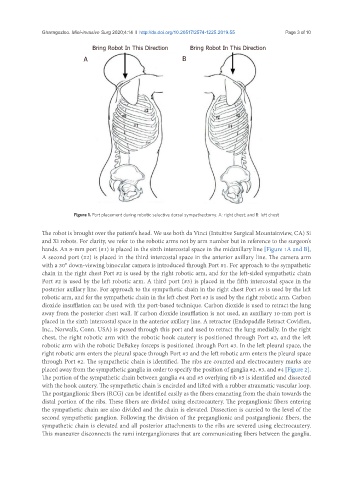
Bring Robot In This Direction Bring Robot In This Direction
A B
Figure 1. Port placement during robotic selective dorsal sympathectomy. A: right chest; and B: left chest
The robot is brought over the patient’s head. We use both da Vinci (Intuitive Surgical Mountainview, CA) Si
and Xi robots. For clarity, we refer to the robotic arms not by arm number but in reference to the surgeon’s
hands. An 8-mm port (#1) is placed in the sixth intercostal space in the midaxillary line [Figure 1A and B],
A second port (#2) is placed in the third intercostal space in the anterior axillary line. The camera arm
with a 30° down-viewing binocular camera is introduced through Port #1. For approach to the sympathetic
chain in the right chest Port #2 is used by the right robotic arm, and for the left-sided sympathetic chain
Port #2 is used by the left robotic arm. A third port (#3) is placed in the fifth intercostal space in the
posterior axillary line. For approach to the sympathetic chain in the right chest Port #3 is used by the left
robotic arm, and for the sympathetic chain in the left chest Port #3 is used by the right robotic arm. Carbon
dioxide insufflation can be used with the port-based technique. Carbon dioxide is used to retract the lung
away from the posterior chest wall. If carbon dioxide insufflation is not used, an auxiliary 10-mm port is
placed in the sixth intercostal space in the anterior axillary line. A retractor (Endopaddle Retract Covidien,
Inc., Norwalk, Conn. USA) is passed through this port and used to retract the lung medially. In the right
chest, the right robotic arm with the robotic hook cautery is positioned through Port #2, and the left
robotic arm with the robotic DeBakey forceps is positioned through Port #3. In the left pleural space, the
right robotic arm enters the pleural space through Port #3 and the left robotic arm enters the pleural space
through Port #2. The sympathetic chain is identified. The ribs are counted and electrocautery marks are
placed away from the sympathetic ganglia in order to specify the position of ganglia #2, #3, and #4 [Figure 2].
The portion of the sympathetic chain between ganglia #4 and #5 overlying rib #5 is identified and dissected
with the hook cautery. The sympathetic chain is encircled and lifted with a rubber atraumatic vascular loop.
The postganglionic fibers (RCG) can be identified easily as the fibers emanating from the chain towards the
distal portion of the ribs. These fibers are divided using electrocautery. The preganglionic fibers entering
the sympathetic chain are also divided and the chain is elevated. Dissection is carried to the level of the
second sympathetic ganglion. Following the division of the preganglionic and postganglionic fibers, the
sympathetic chain is elevated and all posterior attachments to the ribs are severed using electrocautery.
This maneuver disconnects the rami interganglionares that are communicating fibers between the ganglia.