Page 47 - Read Online
P. 47
Koga et al. Minimal laminectomy with the interlaminar approach for PELD
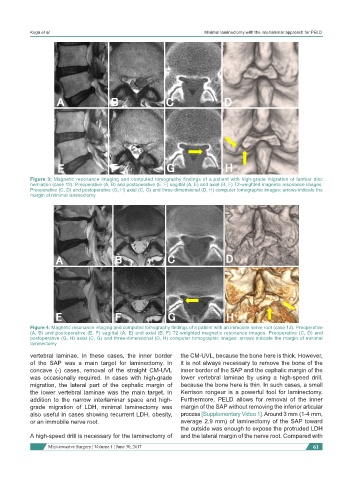
Figure 3: Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography findings of a patient with high-grade migration of lumbar disc
herniation (case 12). Preoperative (A, B) and postoperative (E, F) sagittal (A, E) and axial (B, F) T2-weighted magnetic resonance images.
Preoperative (C, D) and postoperative (G, H) axial (C, G) and three-dimensional (D, H) computer tomographic images: arrows indicate the
margin of minimal laminectomy
Figure 4: Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography findings of a patient with an immobile nerve root (case 13). Preoperative
(A, B) and postoperative (E, F) sagittal (A, E) and axial (B, F) T2-weighted magnetic resonance images. Preoperative (C, D) and
postoperative (G, H) axial (C, G) and three-dimensional (D, H) computer tomographic images: arrows indicate the margin of minimal
laminectomy
vertebral laminae. In these cases, the inner border the CM-UVL, because the bone here is thick. However,
of the SAP was a main target for laminectomy. In it is not always necessary to remove the bone of the
concave (-) cases, removal of the straight CM-UVL inner border of the SAP and the cephalic margin of the
was occasionally required. In cases with high-grade lower vertebral laminae by using a high-speed drill,
migration, the lateral part of the cephalic margin of because the bone here is thin. In such cases, a small
the lower vertebral laminae was the main target. In Kerrison rongeur is a powerful tool for laminectomy.
addition to the narrow interlaminar space and high- Furthermore, PELD allows for removal of the inner
grade migration of LDH, minimal laminectomy was margin of the SAP without removing the inferior articular
also useful in cases showing recurrent LDH, obesity, process [Supplementary Video 1]. Around 3 mm (1-4 mm,
or an immobile nerve root. average 2.9 mm) of laminectomy of the SAP toward
the outside was enough to expose the protruded LDH
A high-speed drill is necessary for the laminectomy of and the lateral margin of the nerve root. Compared with
Mini-invasive Surgery ¦ Volume 1 ¦ June 30, 2017 61