Page 38 - Read Online
P. 38
Ciria et al. Mini-invasive Surg 2024;8:10 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2574-1225.2023.126 Page 5 of 9
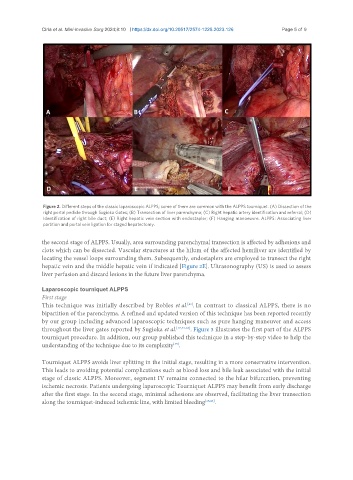
Figure 2. Different steps of the classic laparoscopic ALPPS; some of them are common with the ALPPS tourniquet. (A) Dissection of the
right portal pedicle through Sugioka Gates; (B) Transection of liver parenchyma; (C) Right hepatic artery identification and referral; (D)
Identification of right bile duct; (E) Right hepatic vein section with endostapler; (F) Hanging manoeuvre. ALPPS: Associating liver
partition and portal vein ligation for staged hepatectomy.
the second stage of ALPPS. Usually, area surrounding parenchymal transection is affected by adhesions and
clots which can be dissected. Vascular structures at the hilum of the affected hemiliver are identified by
locating the vessel loops surrounding them. Subsequently, endostaplers are employed to transect the right
hepatic vein and the middle hepatic vein if indicated [Figure 2E]. Ultrasonography (US) is used to assess
liver perfusion and discard lesions in the future liver parenchyma.
Laparoscopic tourniquet ALPPS
First stage
This technique was initially described by Robles et al. . In contrast to classical ALPPS, there is no
[43]
bipartition of the parenchyma. A refined and updated version of this technique has been reported recently
by our group including advanced laparoscopic techniques such as pure hanging maneuver and access
throughout the liver gates reported by Sugioka et al. [17,44-46] . Figure 3 illustrates the first part of the ALPPS
tourniquet procedure. In addition, our group published this technique in a step-by-step video to help the
understanding of the technique due to its complexity .
[45]
Tourniquet ALPPS avoids liver splitting in the initial stage, resulting in a more conservative intervention.
This leads to avoiding potential complications such as blood loss and bile leak associated with the initial
stage of classic ALPPS. Moreover, segment IV remains connected to the hilar bifurcation, preventing
ischemic necrosis. Patients undergoing laparoscopic Tourniquet ALPPS may benefit from early discharge
after the first stage. In the second stage, minimal adhesions are observed, facilitating the liver transection
along the tourniquet-induced ischemic line, with limited bleeding [18,45] .