Page 22 - Read Online
P. 22
Page 56 Ding et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2021;5:50-61 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.01
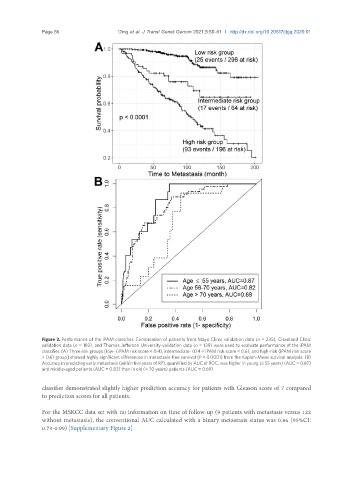
Figure 3. Performance of the iPAM classifier. Combination of patients from Mayo Clinic validation data (n = 235), Cleveland Clinic
validation data (n = 182), and Thomas Jefferson University validation data (n = 139) were used to evaluate performance of the iPAM
classifier. (A) Three risk groups [low- (iPAM risk score < 0.4), intermediate- (0.4 ≤ iPAM risk score ≤ 0.6), and high-risk (iPAM risk score
> 0.6) group] showed highly significant differences in metastasis-free survival (P < 0.0001) from the Kaplan-Meier survival analysis. (B)
Accuracy in predicting early metastasis (within five years of RP), quantified by AUC of ROC, was higher in young (≤ 55 years) (AUC = 0.87)
and middle-aged patients (AUC = 0.82) than in old (> 70 years) patients (AUC = 0.69).
classifier demonstrated slightly higher prediction accuracy for patients with Gleason score of 7 compared
to prediction scores for all patients.
For the MSKCC data set with no information on time of follow-up (9 patients with metastasis versus 122
without metastasis), the conventional AUC calculated with a binary metastasis status was 0.86 (95%CI:
0.73-0.99) [Supplementary Figure 2].