Page 78 - Read Online
P. 78
Goodman et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2020;4:144-58 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2020.23 Page 147
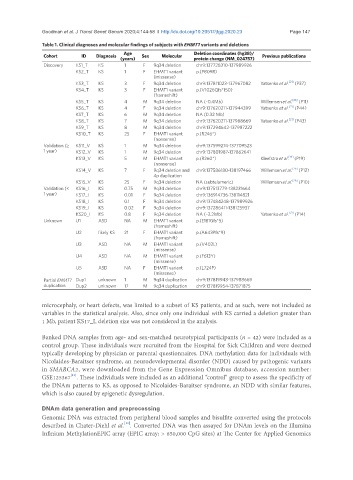
Table 1. Clinical diagnoses and molecular findings of subjects with EHMT1 variants and deletions
Age Deletion coordinates (hg38)/
Cohort ID Diagnosis Sex Molecular Previous publications
(years) protein change (NM_024757)
Discovery KS1_T KS 1 F 9q34 deletion chr9:137728310-137989926
KS2_T KS 1 F EHMT1 variant p.(P809R)
(missense)
KS3_T KS 3 F 9q34 deletion chr9:137811023-137967082 Yatsenko et al. (P37)
[21]
KS4_T KS 3 F EHMT1 variant p.(V1026Qfs*150)
(frameshift)
KS5_T KS 4 M 9q34 deletion NA (~0.4Mb) Willemsen et al. [26] (P11)
[21]
KS6_T KS 4 F 9q34 deletion chr9:137620211-137944399 Yatsenko et al. (P44)
KS7_T KS 6 M 9q34 deletion NA (0.32 Mb)
[21]
KS8_T KS 7 M 9q34 deletion chr9:137620211-137988669 Yatsenko et al. (P43)
KS9_T KS 8 M 9q34 deletion chr9:137294642-137987222
KS10_T KS 25 F EHMT1 variant p.(R246*)
(nonsense)
Validation (≥ KS11_V KS 1 M 9q34 deletion chr9:137599274-137709523
1 year) KS12_V KS 1 M 9q34 deletion chr9:137801987-137862641
KS13_V KS 5 M EHMT1 variant p.(R260*) Kleefstra et al. [19] (P19)
(nonsense)
KS14_V KS 7 F 9q34 deletion and chr9:137586180-138197466 Willemsen et al. [26] (P12)
4p duplication
KS15_V KS 25 F 9q34 deletion NA (subtelomeric) Willemsen et al. [26] (P10)
Validation (< KS16_I KS 0.75 M 9q34 deletion chr9:137513779-138231664
1 year) KS17_I KS 0.01 F 9q34 deletion chr9:136914736-138114821
KS18_I KS 0.1 F 9q34 deletion chr9:137484248-137989926
KS19_I KS 0.02 F 9q34 deletion chr9:137286411-138125937
[21]
KS20_I KS 0.8 F 9q34 deletion NA (~3.2Mb) Yatsenko et al. (P14)
Unknown U1 ASD NA M EHMT1 variant p.(E181Gfs*5)
(frameshift)
U2 likely KS 21 F EHMT1 variant p.(A643Pfs*9)
(frameshift)
U3 ASD NA M EHMT1 variant p.(V402L)
(missense)
U4 ASD NA M EHMT1 variant p.(F613Y)
(missense)
U5 ASD NA F EHMT1 variant p.(L724P)
(missense)
Partial EHMT1 Dup1 unknown 1 M 9q34 duplication chr9:137819943-137988669
duplication Dup2 unknown 17 M 9q34 duplication chr9:137819954-137871875
microcephaly, or heart defects, was limited to a subset of KS patients, and as such, were not included as
variables in the statistical analysis. Also, since only one individual with KS carried a deletion greater than
1 Mb, patient KS17_I, deletion size was not considered in the analysis.
Banked DNA samples from age- and sex-matched neurotypical participants (n = 42) were included as a
control group. These individuals were recruited from the Hospital for Sick Children and were deemed
typically developing by physician or parental questionnaires. DNA methylation data for individuals with
Nicolaides-Baraitser syndrome, an neurodevelopmental disorder (NDD) caused by pathogenic variants
in SMARCA2, were downloaded from the Gene Expression Omnibus database, accession number:
GSE125367 . These individuals were included as an additional “control” group to assess the specificity of
[11]
the DNAm patterns to KS, as opposed to Nicolaides-Baraitser syndrome, an NDD with similar features,
which is also caused by epigenetic dysregulation.
DNAm data generation and preprocessing
Genomic DNA was extracted from peripheral blood samples and bisulfite converted using the protocols
[11]
described in Chater-Diehl et al. . Converted DNA was then assayed for DNAm levels on the Illumina
Infinium MethylationEPIC array (EPIC array; > 850,000 CpG sites) at The Center for Applied Genomics