Page 23 - Read Online
P. 23
Przanowski et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2018;2:2 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2017.03 Page 3 of 15
A X Rnf12 Xist
p
RNF12 Xist
X Rnf12 Xist Xa
m
p
m
m
m
Xa p Xa Xa p Xa Xi Xa
Imprinted XCl
Extraembryonic tissues (Imprinted XCI) Random XCI XCR
B Embryo (Random XCI)
Trophectoderm
p
Xi Xa m
Primitive endoderm
p
Xi Xa m
Tsix Pre-epiblast
p
Xa Xa m
Xist Pluripotency factors
C
Fpx RNF12 Jpx
PRC2
PRC1
Unknown X-linked gene
factors vvv PolII YY1 PolII PRC1 PRC1
PRC2 PRC2
Xist
u1 PRC1
H2AK119
Maternal imprinting Rnf12 gene
Xist gene RNF12 protein (CG) n
Xist RNA vvv YY1 binding motif K H3K27 me
Tsix gene YY1 YY1 protein ac me3
Tsix RNA DNMT1
HDAC PRC2
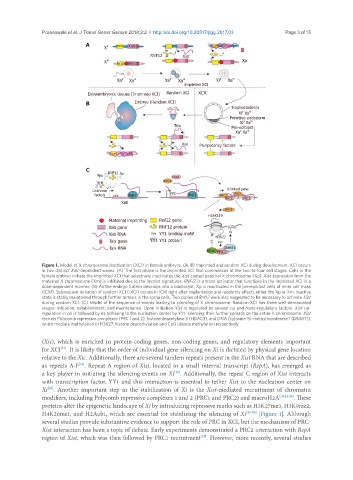
Figure 1. Model of X chromosome inactivation (XCI) in female embryos. (A, B) Imprinted and random XCI during development. XCI occurs
in two distinct Xist-dependent waves. (A) The first phase is the imprinted XCI that commences at the two-to-four cell stages. Cells in the
female embryo initiate the imprinted XCI that selectively inactivates the Xist coated paternal X chromosome (Xp). Xist expression from the
maternal X chromosome (Xm) is inhibited due to the imprint signatures. RNF12 is a trans-activator that functions in the imprinted XCI in a
dose-dependent manner. (B) As the embryo further develops into a blastocyst, Xp is reactivated in the pre-epiblast cells of inner cell mass
(ICM). Subsequent initiation of random XCI (rXCI) occurs in ICM right after implantation and randomly affects either the Xp or Xm. Inactive
state is stably maintained through further mitosis in the soma cells. Two copies of Rnf12 were also suggested to be necessary to activate Xist
during random XCI. (C) Model of the sequence of events leading to silencing of X chromosome. Random XCI has three well-demarcated
stages: initiation, establishment, and maintenance. Upon initiation Xist is regulated by several cis and trans-regulatory factors. Xist up-
regulation in cis is followed by its tethering to the nucleation center by YY1, silencing then further spreads on the entire X chromosome. Xist
recruits Polycomb repressive complexes (PRC 1 and 2), histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3), and DNA (cytosine-5)-methyltransferase 1 (DNMT1),
which mediate methylation of H3K27, histone deacethylation and CpG islands methylation respectively
(Xic), which is enriched in protein-coding genes, non-coding genes, and regulatory elements important
[17]
for XCI . It is likely that the order of individual gene silencing on Xi is dictated by physical gene location
relative to the Xic. Additionally, there are several tandem repeats present in the Xist RNA that are described
as repeats A-F . Repeat A region of Xist, located in a small internal transcript (RepA), has emerged as
[18]
a key player in initiating the silencing events on Xi . Additionally, the repeat C region of Xist interacts
[19]
with transcription factor, YY1 and this interaction is essential to tether Xist to the nucleation center on
Xi . Another important step in the stabilization of Xi is the Xist-mediated recruitment of chromatin
[20]
modifiers, including Polycomb repressive complexes 1 and 2 (PRC1 and PRC2) and macroH2A [19,21,22] . These
proteins alter the epigenetic landscape of Xi by introducing repressive marks such as H3K27me3, H3K9me2,
H4K20me1, and H2Aub1, which are essential for stabilizing the silencing of Xi [23-26] [Figure 1]. Although
several studies provide substantive evidence to support the role of PRC in XCI, but the mechanism of PRC-
Xist interaction has been a topic of debate. Early experiments demonstrated a PRC2 interaction with RepA
region of Xist, which was then followed by PRC1 recruitment . However, more recently, several studies
[27]