Page 108 - Read Online
P. 108
Chu et al. J Transl Genet Genom 2023;7:196-212 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/jtgg.2023.22 Page 102
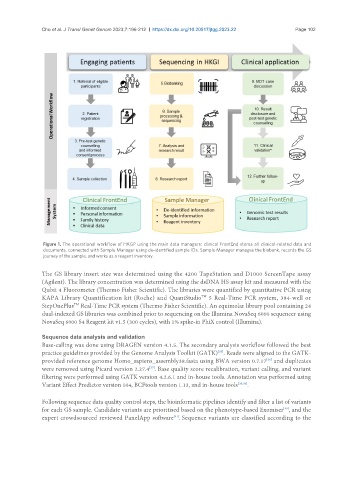
Figure 1. The operational workflow of HKGP using the main data managers: clinical FrontEnd stores all clinical-related data and
documents, connected with Sample Manager using de-identified sample IDs. Sample Manager manages the biobank, records the GS
journey of the sample, and works as a reagent inventory.
The GS library insert size was determined using the 4200 TapeStation and D1000 ScreenTape assay
(Agilent). The library concentration was determined using the dsDNA HS assay kit and measured with the
Qubit 4 Fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific). The libraries were quantified by quantitative PCR using
TM
KAPA Library Quantification kit (Roche) and QuantStudio 5 Real-Time PCR system, 384-well or
StepOnePlus Real-Time PCR system (Thermo Fisher Scientific). An equimolar library pool containing 24
TM
dual-indexed GS libraries was combined prior to sequencing on the Illumina NovaSeq 6000 sequencer using
NovaSeq 6000 S4 Reagent kit v1.5 (300 cycles), with 1% spike-in PhiX control (Illumina).
Sequence data analysis and validation
Base-calling was done using DRAGEN version 4.1.5. The secondary analysis workflow followed the best
practice guidelines provided by the Genome Analysis Toolkit (GATK) . Reads were aligned to the GATK-
[35]
provided reference genome Homo_sapiens_assembly38.fasta using BWA version 0.7.17 and duplicates
[36]
were removed using Picard version 2.27.4 . Base quality score recalibration, variant calling, and variant
[37]
filtering were performed using GATK version 4.2.6.1 and in-house tools. Annotation was performed using
Variant Effect Predictor version 104, BCFtools version 1.13, and in-house tools [38,39] .
Following sequence data quality control steps, the bioinformatic pipelines identify and filter a list of variants
for each GS sample. Candidate variants are prioritised based on the phenotype-based Exomiser , and the
[40]
expert crowdsourced reviewed PanelApp software . Sequence variants are classified according to the
[41]