Page 63 - Read Online
P. 63
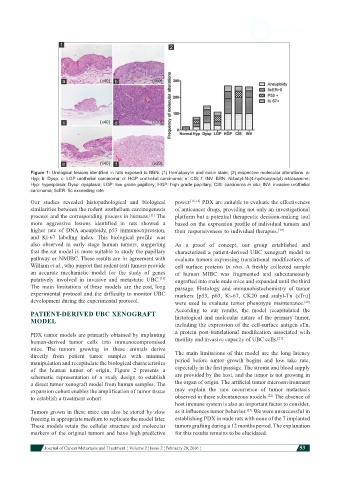
Figure 1: Urological lesions identified in rats exposed to BBN. (1) Hematoxylin and eosin stain; (2) respective molecular alterations. a:
Hyp; b: Dysp; c: LGP urothelial carcinoma; d: HGP urothelial carcinoma; e: CIS; f: INV. BBN: N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl) nitrosamine;
Hyp: hyperplasia; Dysp: dysplasia; LGP: low grade papillary; HGP: high grade papillary; CIS: carcinoma in situ; INV: invasive urothelial
carcinoma; 5cER: 5c exceeding rate
Our studies revealed histopathological and biological power. [16-18] PDX are suitable to evaluate the effectiveness
similarities between the rodent urothelium carcinogenesis of anticancer drugs, providing not only an investigational
process and the corresponding process in humans. The platform but a potential therapeutic decision-making tool
[11]
more aggressive lesions identified in rats showed a based on the expression profile of individual tumors and
higher rate of DNA aneuploidy, p53 immunoexpression, their responsiveness to individual therapies. [19]
and Ki-67 labeling index. This biological profile was
also observed in early stage human tumors, suggesting As a proof of concept, our group established and
that the rat model is more suitable to study the papillary characterized a patient-derived UBC xenograft model to
pathway or NMIBC. These results are in agreement with evaluate tumors expressing translational modifications of
William et al., who purport that rodent (rat) tumors provide cell surface proteins in vivo. A freshly collected sample
an accurate mechanistic model for the study of genes of human MIBC was fragmented and subcutaneously
putatively involved in invasive and metastatic UBC. engrafted into male nude mice and expanded until the third
[15]
The main limitations of these models are the cost, long passage. Histology and immunohistochemistry of tumor
experimental protocol and the difficulty to monitor UBC markers [p53, p63, Ki-67, CK20 and sialyl-Tn (sTn)]
development during the experimental protocol. were used to evaluate tumor phenotype maintenance.
[20]
PATIENT-DERIVED UBC XENOGRAFT According to our results, the model recapitulated the
MODEL histological and molecular nature of the primary tumor,
including the expression of the cell-surface antigen sTn,
PDX tumor models are primarily obtained by implanting a protein post-translational modification associated with
human-derived tumor cells into immunocompromised motility and invasive capacity of UBC cells. [21]
mice. The tumors growing in these animals derive
directly from patient tumor samples with minimal The main limitations of this model are the long latency
manipulation and recapitulate the biological characteristics period before tumor growth begins and low take rate,
of the human tumor of origin. Figure 2 presents a especially in the first passage. The stroma and blood supply
schematic representation of a study design to establish are provided by the host, and the tumor is not growing in
a direct tumor xenograft model from human samples. The the organ of origin. The artificial tumor microenvironment
expansion cohort enables the amplification of tumor tissue may explain the rare occurrence of tumor metastasis
[22]
to establish a treatment cohort. observed in these subcutaneous models. The absence of
host immune system is also an important factor to consider,
Tumors grown in these mice can also be stored by slow as it influences tumor behavior. We were unsuccessful in
[23]
freezing in appropriate medium to replicate the model later. establishing PDX in nude rats with none of the 7 implanted
These models retain the cellular structure and molecular tumors grafting during a 12 months period. The explanation
markers of the original tumors and have high predictive for this results remains to be elucidated.
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ Issue 2 ¦ February 29, 2016 ¦ 53