Page 58 - Read Online
P. 58
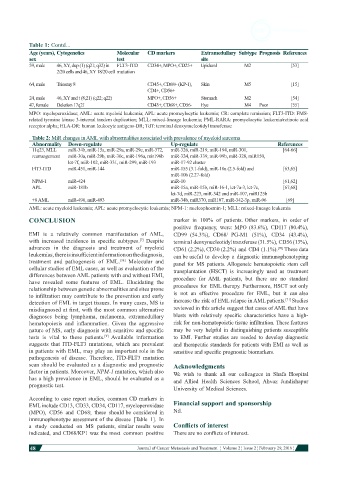
Table 1: Contd...
Age (years), Cytogenetics Molecular CD markers Extramedullary Subtype Prognosis References
sex test site
59, male 46, XY, dup (1) (q21; q32) in FLT3-ITD CD34+, MPO+, CD25+ Epidural M2 [53]
2/20 cells and 46, XY 18/20 cell mutation
64, male Trisomy 8 CD45+, CD68+ (KP-1), Skin M5 [15]
CD4+, CD56+
24, male 46, XY and t (8;21) (q22; q22) MPO+, CD56+ Stomach M2 [54]
47, female Deletion 17q21 CD43+, CD68+, CD56- Eye M4 Poor [55]
MPO: myeloperoxidase; AML: acute myeloid leukemia; APL: acute promeylocytic leukemia; CR: complete remission; FLT3-ITD: FMS-
related tyrosine kinase 3-internal tandem duplication; MLL: mixed-lineage leukemia; PML-RARA: promyelocytic leukemia/retinoic acid
receptor alpha; HLA-DR: human leukocyte antigens-DR; TdT: terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
Table 2: MiR changes in AML with abnormalities associated with prevalence of myeloid sarcoma
Abnormality Down-regulate Up-regulate References
11q23, MLL miR-34b, miR-15a, miR-29a, miR-29c, miR-372, miR-326, miR-219, miR-194, miR-301, [64-66]
rearrangement miR-30a, miR-29b, miR-30e, miR-196a, mir196b miR-324, miR-339, miR-99b, miR-328, miR150,
let-7f, miR-102, miR-331, miR-299, miR-193 miR-17-92 cluster
FlT3-ITD miR-451, miR-144 miR-155 (3.1-fold), miR-10a (2.5-fold) and [63,65]
miR-10b (2.27-fold)
NPM-1 miR-424 miR-10 [61,62]
APL miR-181b miR-15a, miR-15b, miR-16-1, let-7a-3, let-7c, [67,68]
let-7d, miR-223, miR-342 and miR-107, miR125b
+8 AML miR-496, miR-493 miR-34b, miR370, miR107, miR-342-3p, miR-96 [69]
AML: acute myeloid leukemia; APL: acute promyelocytic leukemia; NPM-1: nucleophosmin-1; MLL: mixed-lineage leukemia
CONCLUSION marker in 100% of patients. Other markers, in order of
positive frequency, were: MPO (83.6%), CD117 (80.4%),
EMI is a relatively common manifestation of AML, CD99 (54.3%), CD68/ PG-M1 (51%), CD34 (43.4%),
with increased incidence in specific subtypes. Despite terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (31.5%), CD56 (13%),
[7]
advances in the diagnosis and treatment of myeloid CD61 (2.2%), CD30 (2.2%) and CD4 (1.1%). These data
[70]
leukemias, there is insufficient information on the diagnosis, can be useful to develop a diagnostic immunophenotyping
treatment and pathogenesis of EML. [38] Molecular and panel for MS patients. Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell
cellular studies of EML cases, as well as evaluation of the transplantation (HSCT) is increasingly used as treatment
differences between AML patients with and without EMI, procedure for AML patients, but there are no standard
have revealed some features of EML. Elucidating the
relationship between genetic abnormalities and sites prone procedures for EML therapy. Furthermore, HSCT not only
to infiltration may contribute to the prevention and early is not an effective procedure for EML, but it can also
[71]
detection of EML in target tissues. In many cases, MS is increase the risk of EML relapse in AML patients. Studies
misdiagnosed at first, with the most common alternative reviewed in this article suggest that cases of AML that have
diagnoses being lymphoma, melanoma, extramedullary blasts with relatively specific characteristics have a high-
hematopoiesis and inflammation. Given the aggressive risk for non-hematopoietic tissue infiltration. These features
nature of MS, early diagnosis with sensitive and specific may be very helpful in distinguishing patients susceptible
tests is vital to these patients. Available information to EMI. Further studies are needed to develop diagnostic
[9]
suggests that ITD-FLT3 mutations, which are prevalent and therapeutic standards for patients with EMI as well as
in patients with EML, may play an important role in the sensitive and specific prognostic biomarkers.
pathogenesis of disease. Therefore, ITD-FLT3 mutation
scan should be evaluated as a diagnostic and prognostic Acknowledgments
factor in patients. Moreover, NPM-1 mutation, which also We wish to thank all our colleagues in Shafa Hospital
has a high prevalence in EML, should be evaluated as a and Allied Health Sciences School, Ahvaz Jundishapur
prognostic test.
University of Medical Sciences.
According to case report studies, common CD markers in
EML include CD13, CD33, CD34, CD117, myeloperoxidase Financial support and sponsorship
(MPO), CD56 and CD68; these should be considered in Nil.
immunophenotype assessment of the disease [Table 1]. In
a study conducted on MS patients, similar results were Conflicts of interest
indicated, and CD68/KP1 was the most common positive There are no conflicts of interest.
48
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ Issue 2 ¦ February 29, 2016 ¦