Page 85 - Read Online
P. 85
Patients with diabetes mellitus, hypertension, and to those without cardiovascular diseases (95% CI: 48-327;
cardiovascular diseases (e.g. myocardial infarction, heart P < 0.001). The odds of not receiving CHOP was 9 times
failure, cerebrovascular stroke) were signifi cantly more higher in patients with diabetes mellitus compared to those
common in the CVP group [Table 3]. Among different without diabetes mellitus (95% CI: 3-28; P < 0.001).
comorbidities, cardiovascular diseases, and diabetes
mellitus were the most signifi cant ones that guided regimen Treatment responses and toxicities
selection. The odds of not receiving CHOP were 125 times Patients with CHOP treatment received more
higher in patients with cardiovascular diseases compared chemotherapy cycles than those treated with CVP (median
6 and 3 cycles, respectively; P < 0.001; Table 4).
CR rate was higher in CHOP-treated patients than in
Table 2: Multivariate analysis of the factors that impact
not receiving CHOP treatment CVP-treated patients (69.9% vs. 29.9%; P < 0.001).
Variables in equation OR (95% CI) P More patients received radiotherapy after CHOP
Age (≥ 60 vs. < 60 years) 10.5 (4.6-23.6) < 0.001 treatment achieved CR than CVP-treated patients (22.2%
Comorbidity (yes vs. no) 37.2 (12.6-109.6) < 0.001 vs. 3%; P = 0.001; Table 3). Compared to CVP, CHOP
was associated with signifi cantly higher toxicities (48.4%
CHOP: Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and vs. 23.9%; P < 0.001), particularly fatigue, alopecia,
prednisone; CI: Confi dence interval; OR: Odds ratio
and gastrointestinal tract toxicities. However, early
deaths following one or two chemotherapy courses were
Table 3: Comorbidities among DLBCNHL patients signifi cantly higher in patients with CVP treatment than
receiving CHOP or CVP with CHOP treatment (43.3% vs. 8.6%; P < 0.001).
Comorbidity Sub-group n (%) P Overall survival and event-free survival
CHOP CVP
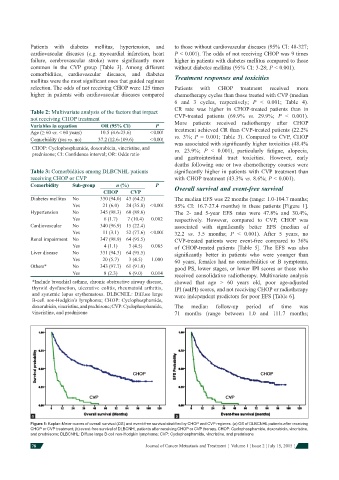
Diabetes mellitus No 330 (94.0) 43 (64.2) The median EFS was 22 months (range: 1.0-104.7 months;
Yes 21 (6.0) 24 (35.8) < 0.001 95% CI: 16.7-27.4 months) in these patients [Figure 1].
Hypertension No 345 (98.3) 60 (89.6) The 2- and 5-year EFS rates were 47.8% and 30.4%,
Yes 6 (1.7) 7 (10.4) 0.002 respectively. However, compared to CVP, CHOP was
Cardiovascular No 340 (96.9) 15 (22.4) associated with signifi cantly better EFS (median of
Yes 11 (3.1) 52 (77.6) < 0.001 32.2 vs. 3.5 months; P < 0.001). After 5 years, no
Renal impairment No 347 (98.9) 64 (95.5) CVP-treated patients were event-free compared to 36%
Yes 4 (1.1) 3 (4.5) 0.085 of CHOP-treated patients [Table 5]. The EFS was also
Liver disease No 331 (94.3) 64 (95.5) signifi cantly better in patients who were younger than
Yes 20 (5.7) 3 (4.5) 1.000 60 years, females had no comorbidities or B symptoms,
Others* No 343 (97.7) 61 (91.0) good PS, lower stages, or lower IPI scores or those who
Yes 8 (2.3) 6 (9.0) 0.014 received consolidative radiotherapy. Multivariate analysis
*Include bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive airway disease, showed that age > 60 years old, poor age-adjusted
thyroid dysfunction, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, IPI (aaIPI) scores, and not receiving CHOP or radiotherapy
and systemic lupus erythematous. DLBCNHL: Diffuse large were independent predictors for poor EFS [Table 6].
B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma; CHOP: Cyclophosphamide,
doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone; CVP: Cyclophosphamide, The median follow-up period of time was
vincristine, and prednisone 71 months (range between 1.0 and 111.7 months;
a b
Figure 1: Kaplan-Meier curves of overall survival (OS) and event-free survival stratifi ed by CHOP and CVP regimes. (a) OS of DLBCNHL patients after receiving
CHOP or CVP treatment; (b) event-free survival of DLBCNHL patients after receiving CHOP or CVP therapy. CHOP: Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine,
and prednisone; DLBCNHL: Diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma; CVP: Cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and prednisone
78 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 1 ¦ Issue 2 ¦ July 15, 2015 ¦