Page 86 - Read Online
P. 86
Table 4: First-line treatments administered to DLBCNHL has been fi rmly established as the most effective single
patients according to their age agent in the treatment of malignant lymphoma. [15,16]
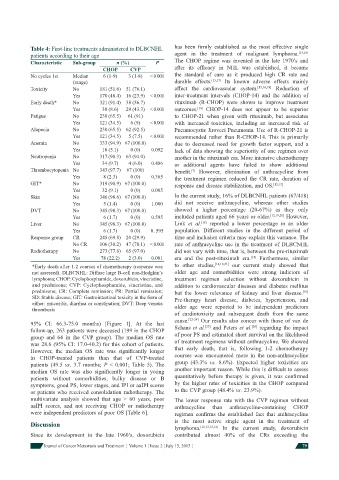
Characteristic Sub-group n (%) P The CHOP regime was invented in the late 1970’s and
CHOP CVP after its effi cacy in NHL was established, it became
No cycles 1st Median 6 (1-9) 3 (1-8) < 0.001 the standard of care as it produced high CR rate and
(range) durable effects. [15,17] Its known adverse effects mainly
Toxicity No 181 (51.6) 51 (76.1) affect the cardiovascular system. [15,16,18] Reduction of
Yes 170 (48.4) 16 (23.9) < 0.001 inter-treatment intervals (CHOP-14) and the addition of
Early death* No 321 (91.4) 38 (56.7) rituximab (R-CHOP) were shown to improve treatment
[16]
Yes 30 (8.6) 29 (43.3) < 0.001 outcomes. CHOP-14 does not appear to be superior
Fatigue No 230 (65.5) 61 (91) to CHOP-21 when given with rituximab, but associates
Yes 121 (34.5) 6 (9) < 0.001 with increased toxicities, including an increased risk of
Alopecia No 230 (65.5) 62 (92.5) Pneumocystis Jiroveci Pneumonia. Use of R-CHOP-21 is
Yes 121 (34.5) 5 (7.5) < 0.001 recommended rather than R-CHOP-14. This is primarily
Anemia No 333 (94.9) 67 (100.0) due to decreased need for growth factor support, and a
Yes 18 (5.1) 0 (0) 0.092 lack of data showing the superiority of one regimen over
Neutropenia No 317 (90.3) 63 (94.0) another in the rituximab era. More intensive chemotherapy
Yes 34 (9.7) 4 (6.0) 0.486 or additional agents have failed to show additional
Thrombocytopenia No 343 (97.7) 67 (100) benefi t. However, elimination of anthracycline from
[7]
Yes 8 (2.3) 0 (0) 0.365 the treatment regimen reduced the CR rate, duration of
GIT* No 319 (90.9) 67 (100.0) response and disease stabilization, and OS. [12,13]
Yes 32 (9.1) 0 (0) 0.005
Skin No 346 (98.6) 67 (100.0) In the current study, 16% of DLBCNHL patients (67/418)
Yes 5 (1.4) 0 (0) 1.000 did not receive anthracycline, whereas other studies
DVT No 345 (98.3) 67 (100.0) showed a higher percentage (20-67%) as they only
Yes 6 (1.7) 0 (0) 0.595 included patients aged 66 years or older. [12,19,20] However,
[18]
Liver No 345 (98.3) 67 (100.0) Link et al. reported a lower percentage in an older
Yes 6 (1.7) 0 (0) 0. 595 population. Different studies in the different period of
Response group CR 245 (69.8) 20 (29.9) time and inclusion criteria may explain this variance. The
No CR 106 (30.2) 47 (70.1) < 0.001 rate of anthracycline use in the treatment of DLBCNHL
Radiotherapy No 273 (77.8) 65 (97.0) did not vary with time, that is, between the pre-rituximab
Yes 78 (22.2) 2 (3.0) 0.001 era and the post-rituximab era. Furthermore, similar
[18]
*Early death after 1-2 courses of chemotherapy (response was to other studies, [18,19,21] our current study showed that
not assessed). DLBCNHL: Diffuse large B-cell non-Hodgkin’s older age and comorbidities were strong indictors of
lymphoma; CHOP: Cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, treatment regimen selection without doxorubicin in
and prednisone; CVP: Cyclophosphamide, vincristine, and addition to cardiovascular diseases and diabetes mellitus
prednisone; CR: Complete remission; PR: Partial remission; but the lower relevance of kidney and liver disease.
[19]
SD: Stable disease; GIT: Gastrointestinal toxicity in the form of Pre-therapy heart disease, diabetes, hypertension, and
either: mucositis, diarrhea or constipation; DVT: Deep venous older age were reported to be independent predictors
thrombosis
of cardiotoxicity and subsequent death from the same
cause. [22-24] Our results also concur with those of van de
95% CI: 66.3-75.0 months) [Figure 1]. At the last [25] [26]
follow-up, 263 patients were deceased (199 in the CHOP Schans et al. and Peters et al. regarding the impact
group and 64 in the CVP group). The median OS rate of poor PS and estimated short survival on the likelihood
was 28.6 (95% CI: 17.0-40.2) for this cohort of patients. of treatment regimens without anthracycline. We showed
However, the median OS rate was signifi cantly longer that early death, that is, following 1-2 chemotherapy
in CHOP-treated patients than that of CVP-treated courses was encountered more in the non-anthracycline
patients (49.5 vs. 3.7 months; P < 0.001; Table 5). The group (43.3% vs. 8.6%). Expected higher toxicities are
median OS rate was also signifi cantly longer in young another important reason. While this is diffi cult to assess
patients without comorbidities, bulky disease or B quantitatively before therapy is given, it was confi rmed
symptoms, good PS, lower stages, and IPI or aaIPI scores by the higher rates of toxicities in the CHOP compared
or patients who received consolidation radiotherapy. The to the CVP group (48.4% vs. 23.9%).
multivariate analysis showed that age > 60 years, poor The lower response rate with the CVP regimen without
aaIPI scores, and not receiving CHOP or radiotherapy anthracycline than anthracycline-containing CHOP
were independent predictors of poor OS [Table 6]. regimen confi rms the established fact that anthracycline
is the most active single agent in the treatment of
Discussion
lymphoma. [12,13,15,16] In the current study, doxorubicin
Since its development in the late 1960’s, doxorubicin contributed almost 40% of the CRs exceeding the
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 1 ¦ Issue 2 ¦ July 15, 2015 ¦ 79