Page 19 - Read Online
P. 19
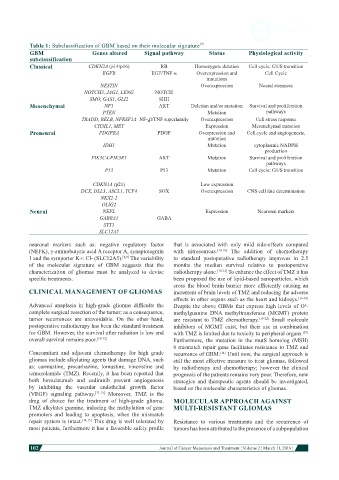
Table 1: Subclassification of GBM based on their molecular signature [9]
GBM Genes altered Signal pathway Status Physiological activity
subclassification
Classical CDKN2A (p14/p16) RB Homozygote deletion Cell cycle: G1/S transition
EGFR EGF/TNF-α Overexpression and Cell Cycle
mutations
NESTIN Overexpression Neural stemness
NOTCH3, JAG1, LENG NOTCH
SMO, GAS1, GLI2 SHH
Mesenchymal NF1 AKT Deletion and/or mutation Survival and proliferation
PTEN Mutation pathways
TRADD, RELB, NFRSF1A NF- K β/TNF superfamily Overexpression Cell stress response
CH3IL1, MET Expression Mesenchymal transtion
Proneural PDGFRA PDGF Overpression and Cell cycle and angiogenesis,
mutation
IDH1 Mutation cytoplasmic NADPH
production
PIK3CA/PIK3R1 AKT Mutation Survival and proliferation
pathways
P53 P53 Mutation Cell cycle: G1/S transition
CDKN1A (p21) Low expression
DCX, DLL3, ASCL1, TCF4 SOX Overexpression CNS cell fate determination
NKX2-2
OLIG2
Neural NEFL Expression Neuronal markers
GABRA1 GABA
SYT1
SLC12A5
neuronal markers such as: negative regulatory factor that is associated with only mild side-effects compared
(NEFK), γ-aminobutyric acid A receptor A, synaptotagmin with nitrosoureas. [10,16] The addition of chemotherapy
1 and the symporter K+: Cl- (SLC12A5). [8,9] The variability to standard postoperative radiotherapy improves in 2.5
of the molecular signature of GBM suggests that the months the median survival relative to postoperative
characterization of gliomas must be analyzed to devise radiotherapy alone. [10-12] To enhance the effect of TMZ it has
specific treatments. been proposed the use of lipid-based nanoparticles, which
cross the blood brain barrier more efficiently causing an
CLINICAL MANAGEMENT OF GLIOMAS increment of brain levels of TMZ and reducing the adverse
effects in other organs such as the heart and kidneys. [16-18]
Advanced anaplasia in high-grade gliomas difficults the Despite the above GBMs that express high levels of O -
6
complete surgical resection of the tumor; as a consequence, methylguanine DNA methyltransferase (MGMT) protein
tumor recurrences are unavoidable. On the other hand, are resistant to TMZ chemotherapy. [19-22] Small molecule
postoperative radiotherapy has been the standard treatment inhibitors of MGMT exist, but their use in combination
for GBM. However, the survival after radiation is low and with TMZ is limited due to toxicity to peripheral organs.
[23]
overall survival remains poor. [10-12] Furthermore, the mutation in the mutS homolog (MSH)
6 mismatch repair gene facilitates resistance to TMZ and
Concomitant and adjuvant chemotherapy for high grade recurrence of GBM. Until now, the surgical approach is
[14]
gliomas include alkylating agents that damage DNA, such still the most effective measure to treat gliomas, followed
as: carmustine, procarbazine, lomustine, vincristine and by radiotherapy and chemotherapy; however the clinical
temozolamide (TMZ). Recently, it has been reported that prognosis of the patients remains very poor. Therefore, new
both bevacizumab and cediranib prevent angiogenesis strategies and therapeutic agents should be investigated,
by inhibiting the vascular endothelial growth factor based on the molecular characteristics of gliomas.
(VEGF) signaling pathway. [11-13] Moreover, TMZ is the
drug of choice for the treatment of high-grade glioma. MOLECULAR APPROACH AGAINST
TMZ alkylates guanine, inducing the methylation of gene MULTI-RESISTANT GLIOMAS
promoters and leading to apoptosis, when the mismatch
repair system is intact. [14,15] This drug is well tolerated by Resistance to various treatments and the recurrence of
most patients, furthermore it has a favorable safety profile tumors has been attributed to the presence of a subpopulation
102
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ March 11, 2016 ¦