Page 22 - Read Online
P. 22
mainly found in neurons and in a more restricted manner in and are considered oncogenes. [105,106] Therefore this would
glial cells in different regions of the CNS of adult mice. suggest that Gas1 could enhance the effect of Shh, inducing
[97]
Furthermore, the expression of Gas1 decreases when the proliferation of glioma and neuroblastoma cells,
neural stem cells are differentiated to a glial phenotype. however we showed that Gas1 inhibits cell proliferation
[98]
However, the role of Gas1 in glial cells is unknown in the of glioma cells even in the presence of the Shh molecular
adult CNS. In hippocampal neurons, Gas1 induces cell death machinery, [107,108] which suggest that in tumors Gas1 inhibits
after excitotoxic insults, inhibiting the signaling induced by the GDNF signaling pathway.
GDNF. [99,100] Nevertheless, during cerebellar development
Gas1 induces the proliferation of cerebellar granule neuron GAS1 INHIBITS THE SIGNALING
progenitors in a Shh-dependent manner. [71,96] INDUCED BY GDNF AND ARTEMIN
Gas1 PROMOTES Shh SIGNALING The GDNF family of ligands (GFLs), GDNF, neurturin
(NRTN), artemin (ARTN) and persephin (PSPN), belong
Shh is a secreted and diffusible morphogen implicated in to a distant branch of the TGF-β superfamily. [109] GFLs
the development of tissues and organs, including the CNS. play a pivotal role in the differentiation and maintenance
The receptor for Shh is Patched (Ptc) which constitutively of both the central and the peripheral nervous system.
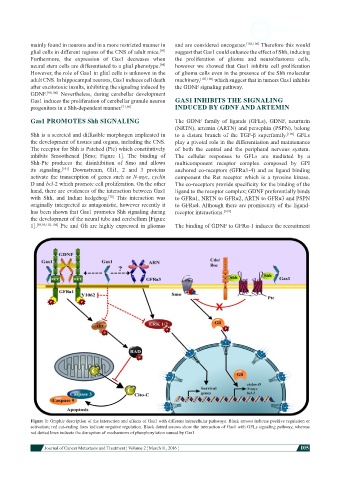
inhibits Smoothened [Smo; Figure 1]. The binding of The cellular responses to GFLs are mediated by a
Shh-Ptc produces the disinhibition of Smo and allows multicomponent receptor complex composed by GPI
its signaling. [101] Downstream, Gli1, 2 and 3 proteins anchored co-receptors (GFRα1-4) and as ligand binding
activate the transcription of genes such as N-myc, cyclin component the Ret receptor which is a tyrosine kinase.
D and bcl-2 which promote cell proliferation. On the other The co-receptors provide specificity for the binding of the
hand, there are evidences of the interaction between Gas1 ligand to the receptor complex; GDNF preferentially binds
with Shh, and Indian hedgehog. This interaction was to GFRα1, NRTN to GFRα2, ARTN to GFRα3 and PSPN
[70]
originally interpreted as antagonistic, however recently it to GFRα4. Although there are promiscuity of the ligand-
has been shown that Gas1 promotes Shh signaling during receptor interactions. [109]
the development of the neural tube and cerebellum [Figure
1]. [89,96,102-104] Ptc and Gli are highly expressed in gliomas The binding of GDNF to GFRα-1 induces the recruitment
Figure 1: Graphic description of the interaction and effects of Gas1 with different intracellular pathways. Black arrows indicate positive regulation or
activation; red cut-ending lines indicate negative regulation. Black dotted arrows show the interaction of Gas1 with GFLs signaling pathway, whereas
red dotted lines indicate the disruption of mechanisms of phosphorylation caused by Gas1
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 2 ¦ March 11, 2016 ¦ 105