Page 49 - Read Online
P. 49
Balakrishnan et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2022;8:27 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2022.33 Page 9 of 17
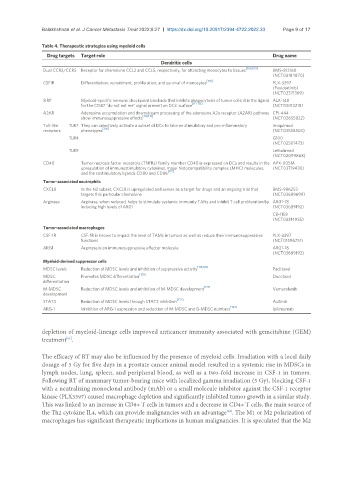
Table 4. Therapeutic strategies using myeloid cells
Drug targets Target role Drug name
Dendritic cells
Dual CCR2/CCR5 Receptor for chemokine CCL2 and CCL5, respectively, for attracting monocytes to tissues [108,109] BMS-813160
(NCT03184870)
CSF1R Differentiation, recruitment, proliferation, and survival of monocytes [110] PLX-3397
(Pexidartinib)
(NCT02371369)
SIRP Myeloid-specific immune checkpoint blockade that inhibits phagocytosis of tumor cells; it is the ligand ALX-148
[111-113]
for the CD47 “do not eat me” signal present on DCs’ surface (NCT03013218)
A2AR Adenosine accumulation and downstream processing of the adenosine A2a receptor (A2AR) pathway CPI-444
[114,115]
show immunosuppressive effects (NCT02655822)
Toll-like TLR7 They can selectively activate a subset of DCs to take on stimulatory and pro-inflammatory Imiquimod
[116]
receptors phenotypes (NCT03558503)
TLR4 G100
(NCT02501473)
TLR9 Lefitolimod
(NCT02099868)
CD40 Tumor necrosis factor receptors (TNFRs) family member CD40 is expressed on DCs and results in the APX-005M
upregulation of immunostimulatory cytokines, major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules, (NCT03719430)
[117]
and the costimulatory ligands CD80 and CD86
Tumor-associated neutrophils
CXCL8 In the N2 subset, CXCL8 is upregulated and serves as a target for drugs and an ongoing trial that BMS-986253
targets this particular chemokine (NCT03689699)
Arginase Arginase, when reduced, helps to stimulate systemic immunity TANs and inhibit T cell proliferation by ARG1-18
inducing high levels of ARG1 (NCT03689192)
CB-1158
(NCT03314935)
Tumor-associated macrophages
CSF-1R CSF-1R is known to impact the level of TAMs in tumors as well as reduce their immunosuppressive PLX-3397
functions (NCT01596751)
ARG1 Arginase is an immunosuppressive effector molecule ARG1-18
(NCT03689192)
Myeloid-derived suppressor cells
[118,119]
MDSC levels Reduction of MDSC levels and inhibition of suppressive activity Paclitaxel
MDSC Promotes MDSC differentiation [120] Docetaxel
differentiation
M-MDSC Reduction of MDSC levels and inhibition of M-MDSC development [121] Vemurafenib
development
STAT3 Reduction of MDSC levels through STAT3 inhibition [122] Axitinib
[123]
ARG-1 Inhibition of ARG-1 expression and reduction of M-MDSC and G-MDSC numbers Ipilimumab
depletion of myeloid-lineage cells improved anticancer immunity associated with gemcitabine (GEM)
treatment .
[91]
The efficacy of RT may also be influenced by the presence of myeloid cells. Irradiation with a local daily
dosage of 3 Gy for five days in a prostate cancer animal model resulted in a systemic rise in MDSCs in
lymph nodes, lung, spleen, and peripheral blood, as well as a two-fold increase in CSF-1 in tumors.
Following RT of mammary tumor-bearing mice with localized gamma irradiation (5 Gy), blocking CSF-1
with a neutralizing monoclonal antibody (mAb) or a small molecule inhibitor against the CSF-1 receptor
kinase (PLX3397) caused macrophage depletion and significantly inhibited tumor growth in a similar study.
This was linked to an increase in CD8+ T cells in tumors and a decrease in CD4+ T cells, the main source of
the Th2 cytokine IL4, which can provide malignancies with an advantage . The M1 or M2 polarization of
[92]
macrophages has significant therapeutic implications in human malignancies. It is speculated that the M2