Page 52 - Read Online
P. 52
Page 12 of 17 Balakrishnan et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2022;8:27 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2022.33
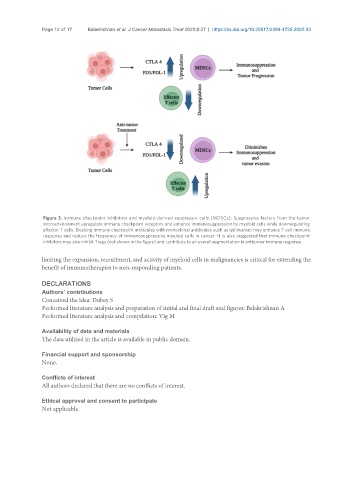
Figure 3. Immune checkpoint inhibitors and myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). Suppressive factors from the tumor
microenvironment upregulate immune checkpoint receptors and enhance immunosuppression by myeloid cells while downregulating
effector T cells. Blocking immune checkpoint molecules with monoclonal antibodies such as ipilimumab may enhance T cell immune
response and reduce the frequency of immunosuppressive myeloid cells in cancer. It is also suggested that immune checkpoint
inhibitors may also inhibit Tregs (not shown in the figure) and contribute to an overall augmentation in antitumor immune response.
limiting the expansion, recruitment, and activity of myeloid cells in malignancies is critical for extending the
benefit of immunotherapies to non-responding patients.
DECLARATIONS
Authors’ contributions
Conceived the idea: Dubey S
Performed literature analysis and preparation of initial and final draft and figures: Balakrishnan A
Performed literature analysis and compilation: Vig M
Availability of data and materials
The data utilized in the article is available in public domain.
Financial support and sponsorship
None.
Conflicts of interest
All authors declared that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.