Page 78 - Read Online
P. 78
García-Pardo et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2021;7:62 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2021.103 Page 15 of 22
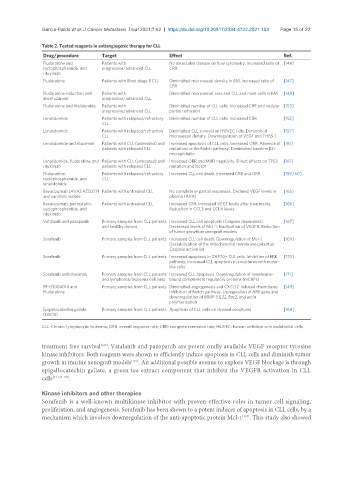
Table 2. Tested reagents in antiangiogenic therapy for CLL
Drug/procedure Target Effect Ref.
Fludarabine and Patients with No detectable disease on flow cytometry. Increased ratio of [146]
cyclophosphamide, and progressive/advanced CLL CRR
rituximab
Fludarabine Patients with Binet stage B CLL Diminished microvessel density in BM. Increased ratio of [147]
CRR
Fludarabine-induction and Patients with Diminished microvessel area and CLL and mast cells in BM [148]
alemtuzumab progressive/advanced CLL
Fludarabine and thalidomide Patients with Diminished number of CLL cells. Increased CRR and nodular [153]
progressive/advanced CLL partial remission
Lenalidomide Patients with relapsed/refractory Diminished number of CLL cells. Increased CRR [155]
CLL
Lenalidomide Patients with relapsed/refractory Diminished CLL survival on HUVEC cells. Diminished [157]
CLL microvessel density. Downregulation of VEGF and THBS-1
Lenalidomide and rituximab Patients with CLL (untreated) and Increased apoptosis of CLL cells. Increased ORR. Absence of [161]
patients with relapsed CLL mutations in the Notch pathway. Diminished baseline β2-
microglobulin
Lenalidomide, fludarabine and Patients with CLL (untreated) and Increased ORR and MRD negativity. Direct effects on TP53 [161]
rituximab patients with relapsed CLL mutation and Notch
Fludarabine, Patients with relapsed/refractory Increased CLL cell death. Increased CRR and ORR [159,160]
cyclophosphamide, and CLL
lenalidomide
Bevacizumab (AVA) AZD2171 Patients with untreated CLL No complete or partial responses. Declined VEGF levels in [165]
and sunitinib malate plasma (AVA)
Bevacizumab, pentostatin, Patients with untreated CLL Increased CRR. Increased VEGF levels after treatments. [166]
cyclophosphamide, and Reduction in CCL3 and CCL4 levels
rituximab
Vatalanib and pazopanib Primary samples from CLL patients Increased CLL cell apoptosis (Caspase dependent). [167]
and healthy donors Decreased levels of Mcl-1. Inactivation of VEGFR. Reduction
of tumor growth in xenograft models
Sorafenib Primary samples from CLL patients Increased CLL cell death. Downregulation of Mcl-1. [169]
Destabilization of the mitochondrial membrane potential.
Caspase activation
Sorafenib Primary samples from CLL patients Increased apoptosis in ZAP70+ CLL cells. Inhibition of ERK [170]
pathway. Increased CLL apoptosis in cocultures with nurse-
like cells
Sorafenib and rituximab Primary samples from CLL patients Increased CLL apoptosis. Downregulation of membrane- [171]
and lymphoma/leukemia cell lines bound complement regulatory proteins (mCRPs)
PF-03084014 and Primary samples from CLL patients Diminished angiogenesis and CXCL12-induced chemotaxis. [149]
Fludarabine Inhibition of Notch pathway. Upregulation of HRK gene and
downregulation of MMP-9,IL32, Rac2, and actin
polymerization
Epigallocatechin gallate Primary samples from CLL patients Apoptosis of CLL cells on stromal cocultures [168]
(EGCG)
CLL: Chronic lymphocytic leukemia; ORR: overall response rate; CRR: complete remission rate; HUVEC: human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
treatment free survival . Vatalanib and pazopanib are potent orally available VEGF receptor tyrosine
[166]
kinase inhibitors. Both reagents were shown to efficiently induce apoptosis in CLL cells and diminish tumor
growth in murine xenograft models . An additional possible avenue to explore VEGF blockage is through
[167]
epigallocatechin gallate, a green tea extract component that inhibits the VEGFR activation in CLL
cells [34,134,168] .
Kinase inhibitors and other therapies
Sorafenib is a well-known multikinase inhibitor with proven effective roles in tumor cell signaling,
proliferation, and angiogenesis. Sorafenib has been shown to a potent inducer of apoptosis in CLL cells, by a
[169]
mechanism which involves downregulation of the anti-apoptotic protein Mcl-1 . This study also showed