Page 32 - Read Online
P. 32
Wenner et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:33 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.73 Page 11 of 17
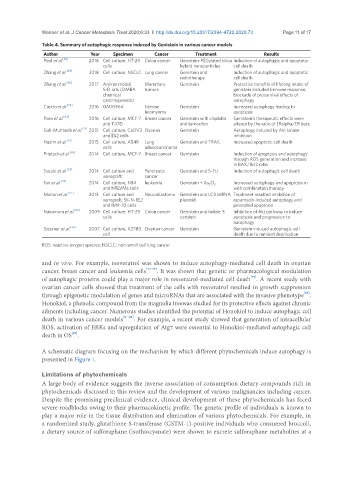
Table 4. Summary of autophagic response induced by Genistein in various cancer models
Author Year Specimen Cancer Treatment Results
Pool et al. [68] 2018 Cell culture, HT-29 Colon cancer Genistein-PEGylated silica Induction of autophagic and apoptotic
cells hybrid nanoparticles cell death
Zhang et al. [69] 2018 Cell culture, NSCLC Lung cancer Genistein and Induction of autophagic and apoptotic
radiotherapy cell death
Zhang et al. [65] 2017 Animal model, Mammary Genistein Protective benefits of lifelong intake of
S-D rats (DMBA tumors genistein included immune response,
chemical blockade of prosurvival effects of
carcinogenesis) autophagy
Castro et al. [72] 2016 GM10964 Uterine Genistein Increased autophagy leading to
leiomyoma apoptosis
Pons et al. [64] 2016 Cell culture, MCF-7 Breast cancer Genistein with cisplatin Genistein’s therapeutic effects were
and T47D and tamoxifen altered by the ratio of ERalpha/ER beta
Gali-Muhtasib et al. [71] 2015 Cell culture, CaOV3 Ovarian Genistein Autophagy induced by Akt kinase
and ES2 cells inhibition
Nazim et al. [61] 2015 Cell culture, A549 Lung Genistein and TRAIL Increased apoptotic cell death
cells adenocarcinoma
Prietsch et al. [63] 2014 Cell culture, MCF-7 Breast cancer Genistein Induction of apoptosis and autophagy
through ROS generation and increase
in BAX/Bcl2 ratio
Suzuki et al. [62] 2014 Cell culture and Pancreatic Genistein and 5-FU Induction of autophagic cell death
xenograft; cancer
Fan et al. [70] 2014 Cell culture, NB4 leukemia Genistein + As 2 O 3 Increased autophagy and apoptosis in
and NRLVMs cells with combination therapy
Mohan et al. [67] 2013 Cell culture and Neuroblastoma Genistein and LC3 shRNA Treatment resulted inhibition of
xenograft; SK-N-BE2 plasmid rapamycin-induced autophagy and
and IMR-32 cells promoted apoptosis
Nakamura et al. [66] 2009 Cell culture, HT-29 Colon cancer Genistein and Indole-3 Inhibition of Akt pathway to induce
cells carbinol apoptosis and progression to
autophagy
Gossner et al. [60] 2007 Cell culture, A2780 Ovarian cancer Genistein Genistein induced autophagic cell
cell death due to nutrient deprivation
ROS: reactive oxygen species; NSCLC: non-small cell lung cancer
and in vivo. For example, resveratrol was shown to induce autophagy-mediated cell death in ovarian
cancer, breast cancer and leukemia cells [76-78] . It was shown that genetic or pharmacological modulation
of autophagic proteins could play a major role in resveratrol-mediated cell death . A recent study with
[79]
ovarian cancer cells showed that treatment of the cells with resveratrol resulted in growth suppression
[80]
through epigenetic modulation of genes and microRNAs that are associated with the invasive phenotype .
Honokiol, a phenolic compound from the magnolia treewas studied for its protective effects against chronic
ailments including cancer. Numerous studies identified the potential of Honokiol to induce autophagic cell
death in various cancer models [81-84] . For example, a recent study showed that generation of intracellular
ROS, activation of ERKs and upregulation of Atg7 were essential to Honokiol-mediated autophagic cell
[85]
death in OS .
A schematic diagram focusing on the mechanism by which different phytochemicals induce autophagy is
presented in Figure 1.
Limitations of phytochemicals
A large body of evidence suggests the inverse association of consumption dietary compounds rich in
phytochemicals discussed in this review and the development of various malignancies including cancer.
Despite the promising preclinical evidence, clinical development of these phytochemicals has faced
severe roadblocks owing to their pharmacokinetic profile. The genetic profile of individuals is known to
play a major role in the tissue distribution and elimination of various phytochemicals. For example, in
a randomized study, glutathione S-transferase (GSTM-1)-positive individuals who consumed broccoli,
a dietary source of sulforaphane (isothiocyanate) were shown to excrete sulforaphane metabolites at a