Page 28 - Read Online
P. 28
Wenner et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2020;6:33 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2020.73 Page 7 of 17
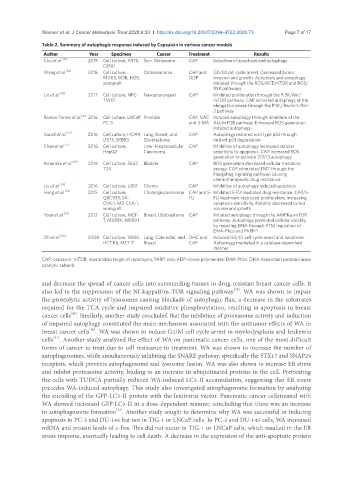
Table 2. Summary of autophagic response induced by Capsaicin in various cancer models
Author Year Specimen Cancer Treatment Results
Chu et al. [38] 2019 Cell culture, A375, Skin: Melanoma CAP Induction of apoptosis and autophagy
C8161
Wang et al. [32] 2018 Cell culture, Osteosarcoma CAP and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest. Decreased tumor
MG63, 143B, HOS, DDP invasion and growth. Apoptosis and autophagy
xenograft initiated through the ROS/AKT/mTOR and ROS/
JNK pathways
Lin et al. [42] 2017 Cell culture, NPC- Nasopharyngeal CAP Inhibited proliferation through the PI3K/Akt/
TW01 mTOR pathway. CAP activated autophagy at the
elongation phase through the PI3K/Beclin-1/Bcl-
2 pathway
Ramos-Torres et al. [41] 2016 Cell culture, LNCaP, Prostate CAP, NAC Induced autophagy through inhibition of the
PC-3 and 3-MA Akt/mTOR pathway. Enhanced ROS generation
induced autophagy
Garufi et al. [34] 2016 Cell culture, H1299, Lung, Breast, and CAP Autophagy restored wild type p53 through
U373, SKBR3 Glioblastoma mutant p53 degradation
Chen et al. [37] 2016 Cell culture, Liver: Hepatocellular CAP Inhibition of autophagy increased cellular
HepG2 Carcinoma sensitivity to apoptosis. CAP increased ROS
generation to activate STAT3 autophagy
Amantini et al. [39] 2016 Cell culture, 5637, Bladder CAP ROS generation decreased cellular metabolic
T24 energy. CAP stimulated EMT through the
Hedgehog signaling pathway, causing
chemotherapeutic drug resistance
Liu et al. [36] 2016 Cell culture, U251 Glioma CAP Inhibition of autophagy induced apoptosis
Hong et al. [33] 2015 Cell culture, Cholangiocarcinoma CAP and 5- Inhibited 5-FU mediated drug resistance. CAP/5-
QBC939, SK- FU FU treatment restricted proliferation, increasing
ChA-1, MZ-ChA-1, apoptosis sensitivity. Notably decreased tumor
xenograft volume and growth
Yoon et al. [35] 2012 Cell culture, MCF- Breast, Glioblastoma CAP Initiated autophagy through the AMPKα-mTOR
7, M059K, M059J pathway. Autophagy promoted cellular viability
by repairing DNA through ATM regulation of
DNA-PKcs and PARP-1
Oh et al. [40] 2008 Cell culture, WI38, Lung, Colorectal, and DHC and Induced G0/G1 cell cycle arrest and apoptosis.
HCT116, MCF-7 Breast CAP Autophagy mediated in a catalase dependent
manner
CAP: capsaicin; mTOR: mammalian target of rapamycin; PARP: poly ADP-ribose polymerase; DNA-PKcs: DNA-dependent protein kinase
catalytic subunit
and decrease the spread of cancer cells into surrounding tissues in drug-resistant breast cancer cells. It
[48]
also led to the suppression of the Nf-kappaB/m-TOR signaling pathway . WA was shown to impair
the proteolytic activity of lysosomes causing blockade of autophagic flux, a decrease in the substrates
required for the TCA cycle and impaired oxidative phosphorylation, resulting in apoptosis in breast
cancer cells . Similarly, another study concluded that the inhibition of proteasome activity and induction
[49]
of impaired autophagy constituted the main mechanism associated with the antitumor effects of WA in
[50]
breast cancer cells . WA was shown to induce G2/M cell cycle arrest in myelodysplasia and leukemia
[51]
cells . Another study analyzed the effect of WA on pancreatic cancer cells, one of the most difficult
forms of cancer to treat due to cell resistance to treatment. WA was shown to increase the number of
autophagosomes, while simultaneously inhibiting the SNARE pathway, specifically the STX17 and SNAP29
receptors, which prevents autophagosome and lysosome fusion. WA was also shown to increase ER stress
and inhibit proteasome activity, leading to an increase in ubiquitinated proteins in the cell. Pretreating
the cells with TUDCA partially reduced WA-induced LC3-II accumulation, suggesting that ER stress
precedes WA-induced autophagy. This study also investigated autophagosome formation by analyzing
the encoding of the GFP-LC3-II protein with the lentivirus vector. Pancreatic cancer cellstreated with
WA showed increased GFP-LC3-II in a dose-dependent manner, concluding that there was an increase
in autophagosome formation . Another study sought to determine why WA was successful in inducing
[52]
apoptosis in PC-3 and DU-145 but not in TIG-1 or LNCaP cells. In PC-3 and DU-145 cells, WA increased
mRNA and protein levels of c-Fos. This did not occur in TIG-1 or LNCaP cells, which resulted in the ER
stress response, eventually leading to cell death. A decrease in the expression of the anti-apoptotic protein