Page 52 - Read Online
P. 52
Farlow et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:18 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.100 Page 5 of 10
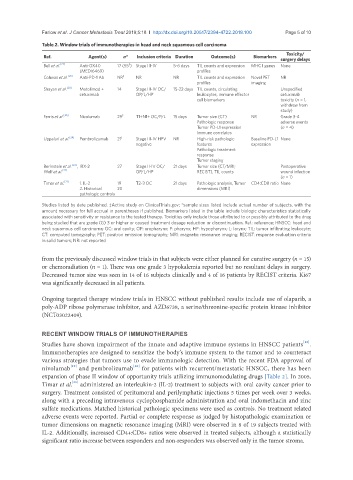
Table 2. Window trials of immunotherapies in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Ref. Agent(s) n* Inclusion criteria Duration Outcome(s) Biomarkers Toxicity/
surgery delays
‡
Bell et al. [27] Anti-OX40 17 (55 ) Stage III-IV 5-6 days TIL counts and expression MHC I genes None
(MEDI6469) profiles
Colevas et al. [26] Anti-PD-1 Ab NR ‡ NR NR TIL counts and expression Novel PET NR
profiles imaging
Shayan et al. [28] Motolimod + 14 Stage III-IV OC/ 15-22 days TIL counts, circulating Unspecified
cetuximab OP/L/HP leukocytes, immune effector cetuximab
cell biomarkers toxicity (n = 1,
withdrew from
study)
Ferris et al. [25] Nivolumab 29 ‡ T1+N1+ OC/P/L 15 days Tumor size (CT) NR Grade 3-4
Pathologic response adverse events
Tumor PD-L1 expression (n = 4)
Immune correlates
Uppaluri et al. [24] Pembrolizumab 21 ‡ Stage III-IV HPV NR High-risk pathologic Baseline PD-L1 None
negative features expression
Pathologic treatment
response
Tumor staging
Berinstein et al. [23] , IRX-2 27 Stage II-IV OC/ 21 days Tumor size (CT/MRI; Postoperative
Wolf et al. [22] OP/L/HP RECIST), TIL counts wound infection
(n = 1)
Timar et al. [21] 1. IL-2 19 T2-3 OC 21 days Pathologic analysis, Tumor CD4:CD8 ratio None
2. Historical 20 dimensions (MRI)
pathologic controls
Studies listed by date published. ‡Active study on ClinicalTrials.gov; *sample sizes listed include actual number of subjects, with the
amount necessary for full accrual in parentheses if published. Biomarkers listed in the table include biologic characteristics statistically
associated with sensitivity or resistance to the tested therapy. Toxicities only include those attributed to or possibly attributed to the drug
being studied that are grade (G) 3 or higher or caused treatment dosage reduction or discontinuation. Ref.: reference; HNSCC: head and
neck squamous cell carcinoma; OC: oral cavity; OP: oropharynx; P: pharynx; HP: hypopharynx; L: larynx; TIL: tumor infiltrating leukocyte;
CT: computed tomography; PET: positron emission tomography; MRI: magnetic resonance imaging; RECIST: response evaluation criteria
in solid tumors; NR: not reported
from the previously discussed window trials in that subjects were either planned for curative surgery (n = 15)
or chemoradiation (n = 1). There was one grade 3 hypokalemia reported but no resultant delays in surgery.
Decreased tumor size was seen in 14 of 16 subjects clinically and 4 of 16 patients by RECIST criteria. Ki67
was significantly decreased in all patients.
Ongoing targeted therapy window trials in HNSCC without published results include use of olaparib, a
poly-ADP ribose polymerase inhibitor, and AZD6738, a serine/threonine-specific protein kinase inhibitor
(NCT03022409).
RECENT WINDOW TRIALS OF IMMUNOTHERAPIES
[18]
Studies have shown impairment of the innate and adaptive immune systems in HNSCC patients .
Immunotherapies are designed to sensitize the body’s immune system to the tumor and to counteract
various strategies that tumors use to evade immunologic detection. With the recent FDA approval of
[19]
nivolumab and pembrolizumab for patients with recurrent/metastatic HNSCC, there has been
[20]
expansion of phase II window of opportunity trials utilizing immunomodulating drugs [Table 2]. In 2005,
Timar et al. administered an interleukin-2 (IL-2) treatment to subjects with oral cavity cancer prior to
[21]
surgery. Treatment consisted of peritumoral and perilymphatic injections 5 times per week over 3 weeks,
along with a preceding intravenous cyclophosphamide administration and oral indomethacin and zinc
sulfate medications. Matched historical pathologic specimens were used as controls. No treatment related
adverse events were reported. Partial or complete response as judged by histopathologic examination or
tumor dimensions on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) were observed in 8 of 19 subjects treated with
IL-2. Additionally, increased CD4+:CD8+ ratios were observed in treated subjects, although a statistically
significant ratio increase between responders and non-responders was observed only in the tumor stroma.