Page 54 - Read Online
P. 54
Farlow et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:18 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.100 Page 7 of 10
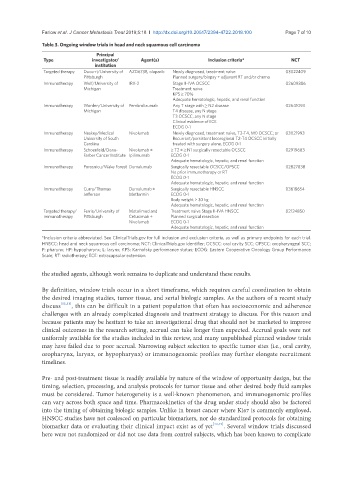
Table 3. Ongoing window trials in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
Principal
Type investigator/ Agent(s) Inclusion criteria* NCT
institution
Targeted therapy Duvurri/University of AZD6738, olaparib Newly diagnosed, treatment naive 03022409
Pittsburgh Planned surgery/biopsy + adjuvant RT and/or chemo
Immunotherapy Wolf/University of IRX-2 Stage II-IVA OCSCC 02609386
Michigan Treatment naive
KPS ≥ 70%
Adequate hematologic, hepatic, and renal function
Immunotherapy Worden/University of Pembrolizumab Any T stage with ≥ N2 disease 02641093
Michigan T4 disease, any N stage
T3 OCSCC, any N stage
Clinical evidence of ECE
ECOG 0-1
Immunotherapy Neskey/Medical Nivolumab Newly diagnosed, treatment naive, T2-T4, M0 OCSCC; or 03021993
University of South Recurrent/persistent locoregional T2-T4 OCSCC initially
Carolina treated with surgery alone, ECOG 0-1
Immunotherapy Schoenfeld/Dana- Nivolumab ± ≥ T2 ± ≥ N1 surgically resectable OCSCC 02919683
Farber Cancer Institute Ipilimumab ECOG 0-1
Adequate hematologic, hepatic, and renal function
Immunotherapy Porosnicu/Wake Forest Durvalumab Surgically resectable OCSCC/OPSCC 02827838
No prior immunotherapy or RT
ECOG 0-1
Adequate hematologic, hepatic, and renal function
Immunotherapy Curry/Thomas Durvalumab ± Surgically resectable HNSCC 03618654
Jefferson Metformin ECOG 0-1
Body weight > 30 kg
Adequate hematologic, hepatic, and renal function
Targeted therapy/ Ferris/University of Motolimod and Treatment naive Stage II-IVA HNSCC 02124850
immunotherapy Pittsburgh Cetuximab ± Planned surgical resection
Nivolumab ECOG 0-1
Adequate hematologic, hepatic, and renal function
*Inclusion criteria abbreviated. See ClinicalTrials.gov for full inclusion and exclusion criteria, as well as primary endpoints for each trial.
HNSCC: head and neck squamous cell carcinoma; NCT: ClinicalTrials.gov identifier; OCSCC: oral cavity SCC; OPSCC: oropharyngeal SCC;
P: pharynx; HP: hypopharynx; L: larynx; KPS: Karnofsky performance status; ECOG: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance
Scale; RT: radiotherapy; ECE: extracapsular extension
the studied agents, although work remains to duplicate and understand these results.
By definition, window trials occur in a short timeframe, which requires careful coordination to obtain
the desired imaging studies, tumor tissue, and serial biologic samples. As the authors of a recent study
discuss [15,31] , this can be difficult in a patient population that often has socioeconomic and adherence
challenges with an already complicated diagnosis and treatment strategy to discuss. For this reason and
because patients may be hesitant to take an investigational drug that should not be marketed to improve
clinical outcomes in the research setting, accrual can take longer than expected. Accrual goals were not
uniformly available for the studies included in this review, and many unpublished planned window trials
may have failed due to poor accrual. Narrowing subject selection to specific tumor sites (i.e., oral cavity,
oropharynx, larynx, or hypopharynx) or immunogenomic profiles may further elongate recruitment
timelines.
Pre- and post-treatment tissue is readily available by nature of the window of opportunity design, but the
timing, selection, processing, and analysis protocols for tumor tissue and other desired body fluid samples
must be considered. Tumor heterogeneity is a well-known phenomenon, and immunogenomic profiles
can vary across both space and time. Pharmacokinetics of the drug under study should also be factored
into the timing of obtaining biologic samples. Unlike in breast cancer where Ki67 is commonly employed,
HNSCC studies have not coalesced on particular biomarkers, nor do standardized protocols for obtaining
biomarker data or evaluating their clinical impact exist as of yet [14,15] . Several window trials discussed
here were not randomized or did not use data from control subjects, which has been known to complicate