Page 87 - Read Online
P. 87
Page 4 of 6 Kurt et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:8 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.80
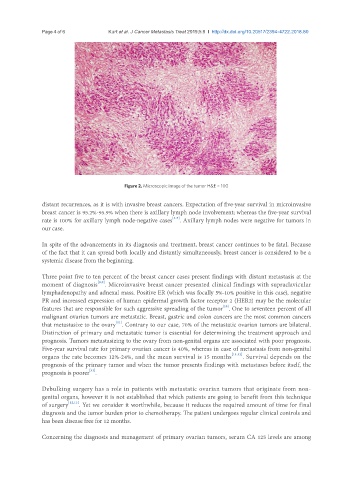
Figure 2. Microscopic image of the tumor H&E × 100
distant recurrences, as it is with invasive breast cancers. Expectation of five-year survival in microinvasive
breast cancer is 95.2%-95.9% when there is axillary lymph node involvement; whereas the five-year survival
[3-7]
rate is 100% for axillary lymph node-negative cases . Axillary lymph nodes were negative for tumors in
our case.
In spite of the advancements in its diagnosis and treatment, breast cancer continues to be fatal. Because
of the fact that it can spread both locally and distantly simultaneously, breast cancer is considered to be a
systemic disease from the beginning.
Three point five to ten percent of the breast cancer cases present findings with distant metastasis at the
[8,9]
moment of diagnosis . Microinvasive breast cancer presented clinical findings with supraclavicular
lymphadenopathy and adnexal mass. Positive ER (which was focally 5%-10% positive in this case), negative
PR and increased expression of human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) may be the molecular
[10]
features that are responsible for such aggressive spreading of the tumor . One to seventeen percent of all
malignant ovarian tumors are metastatic. Breast, gastric and colon cancers are the most common cancers
[11]
that metastasize to the ovary . Contrary to our case, 70% of the metastatic ovarian tumors are bilateral.
Distinction of primary and metastatic tumor is essential for determining the treatment approach and
prognosis. Tumors metastasizing to the ovary from non-genital organs are associated with poor prognosis.
Five-year survival rate for primary ovarian cancer is 40%, whereas in case of metastasis from non-genital
organs the rate becomes 12%-24%, and the mean survival is 15 months [11,12] . Survival depends on the
prognosis of the primary tumor and when the tumor presents findings with metastases before itself, the
[12]
prognosis is poorer .
Debulking surgery has a role in patients with metastatic ovarian tumors that originate from non-
genital organs, however it is not established that which patients are going to benefit from this technique
of surgery [12,13] . Yet we consider it worthwhile, because it reduces the required amount of time for final
diagnosis and the tumor burden prior to chemotherapy. The patient undergoes regular clinical controls and
has been disease free for 12 months.
Concerning the diagnosis and management of primary ovarian tumors, serum CA 125 levels are among