Page 159 - Read Online
P. 159
Mooney et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:19 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.93 Page 7 of 17
A
B
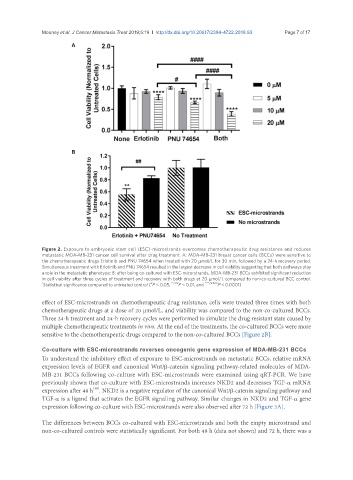
Figure 2. Exposure to embryonic stem cell (ESC)-microstrands overcomes chemotherapeutic drug resistance and reduces
metastatic MDA-MB-231 cancer cell survival after drug treatment. A: MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells (BCCs) were sensitive to
the chemotherapeutic drugs Erlotinib and PNU 74654 when treated with 20 μmol/L for 30 min, followed by a 24-h recovery period.
Simultaneous treatment with Erlotinib and PNU 74654 resulted in the largest decrease in cell viability suggesting that both pathways play
a role in the metastatic phenotype; B: after being co-cultured with ESC-micorstrands, MDA-MB-231 BCCs exhibited significant reduction
in cell viability after three cycles of treatment and recovery with both drugs at 20 μmol/L compared to non-co-cultured BCC control.
#
* Statistical significance compared to untreated control ( P < 0.05, **/## P < 0.01, and ****/#### P < 0.0001)
effect of ESC-microstrands on chemotherapeutic drug resistance, cells were treated three times with both
chemotherapeutic drugs at a dose of 20 µmol/L, and viability was compared to the non-co-cultured BCCs.
Three 24-h treatment and 24-h recovery cycles were performed to simulate the drug resistant state caused by
multiple chemotherapeutic treatments in vivo. At the end of the treatments, the co-cultured BCCs were more
sensitive to the chemotherapeutic drugs compared to the non-co-cultured BCCs [Figure 2B].
Co-culture with ESC-microstrands reverses oncogenic gene expression of MDA-MB-231 BCCs
To understand the inhibitory effect of exposure to ESC-microstrands on metastatic BCCs, relative mRNA
expression levels of EGFR and canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway-related molecules of MDA-
MB-231 BCCs following co-culture with ESC-microstrands were examined using qRT-PCR. We have
previously shown that co-culture with ESC-microstrands increases NKD2 and decreases TGF-α mRNA
[10]
expression after 48 h . NKD2 is a negative regulator of the canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway and
TGF-α is a ligand that activates the EGFR signaling pathway. Similar changes in NKD2 and TGF-α gene
expression following co-culture with ESC-microstrands were also observed after 72 h [Figure 3A].
The differences between BCCs co-cultured with ESC-microstrands and both the empty microstrand and
non-co-cultured controls were statistically significant. For both 48 h (data not shown) and 72 h, there was a