Page 64 - Read Online
P. 64
Narayanan et al. J Cancer Metastasis Treat 2019;5:36 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-4722.2018.77 Page 7 of 11
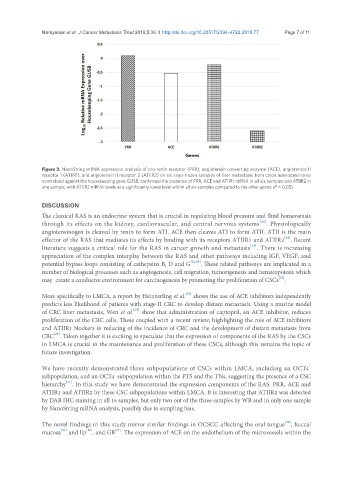
Figure 3. NanoString mRNA expression analysis of pro-renin receptor (PRR), angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE), angiotensin II
receptor 1 (ATIIR1), and angiotensin II receptor 2 (ATIIR2) on six snap-frozen samples of liver metastasis from colon adenocarcinoma
normalized against the housekeeping gene GUSB, confirmed the presence of PRR, ACE and ATIIR1 mRNA in all six samples and ATIIR2 in
one sample, with ATIIR2 mRNA levels at a significantly lower level within all six samples compared to the other genes (P < 0.05)
DISCUSSION
The classical RAS is an endocrine system that is crucial in regulating blood pressure and fluid homeostasis
[24]
through its effects on the kidney, cardiovascular, and central nervous systems . Physiologically
angiotensinogen is cleaved by renin to form ATI. ACE then cleaves ATI to form ATII. ATII is the main
[24]
effector of the RAS that mediates its effects by binding with its receptors ATIIR1 and ATIIR2 . Recent
[24]
literature suggests a critical role for the RAS in cancer growth and metastasis . There is increasing
appreciation of the complex interplay between the RAS and other pathways including IGF, VEGF, and
potential bypass loops consisting of cathepsins B, D and G [22,34] . These related pathways are implicated in a
number of biological processes such as angiogenesis, cell migration, tumorigenesis and hematopoiesis which
[22]
may create a conducive environment for carcinogenesis by promoting the proliferation of CSCs .
[26]
More specifically to LMCA, a report by Heinzerling et al. shows the use of ACE inhibitors independently
predicts less likelihood of patients with stage II CRC to develop distant metastasis. Using a murine model
[35]
of CRC liver metastasis, Wen et al. show that administration of captopril, an ACE inhibitor, reduces
proliferation of the CRC cells. These coupled with a recent review, highlighting the role of ACE inhibitors
and ATIIR1 blockers in reducing of the incidence of CRC and the development of distant metastasis from
[25]
CRC . Taken together it is exciting to speculate that the expression of components of the RAS by the CSCs
in LMCA is crucial in the maintenance and proliferation of these CSCs, although this remains the topic of
future investigation.
+
We have recently demonstrated three subpopulations of CSCs within LMCA, including an OCT4
-
subpopulation, and an OCT4 subpopulation within the PTS and the TNs, suggesting the presence of a CSC
[21]
hierarchy . In this study we have demonstrated the expression components of the RAS: PRR, ACE and
ATIIR1 and ATIIR2 by these CSC subpopulations within LMCA. It is interesting that ATIIR2 was detected
by DAB IHC staining in all 16 samples, but only two out of the three samples by WB and in only one sample
by NanoString mRNA analysis, possibly due to sampling bias.
[28]
The novel findings in this study mirror similar findings in OCSCC affecting the oral tongue , buccal
[27]
[16]
[17]
mucosa and lip , and GB . The expression of ACE on the endothelium of the microvessels within the