Page 98 - Read Online
P. 98
Falconer et al. MT-MMPs in prostate cancer
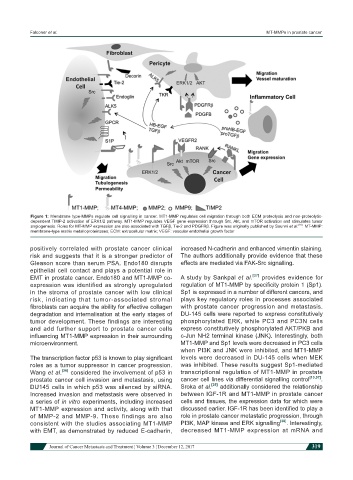
Figure 1: Membrane type-MMPs regulate cell signalling in cancer. MT1-MMP regulates cell migration through both ECM proteolysis and non-proteolytic-
dependent TIMP-2 activation of ERK1/2 pathway. MT1-MMP regulates VEGF gene expression through Src, Akt, and mTOR activation and stimulates tumor
[28]
angiogenesis. Roles for MT-MMP expression are also associated with TGFβ, Tie-2 and PDGFRβ. Figure was originally published by Sounni et al. . MT-MMP:
membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases; ECM: extracellular matrix; VEGF: vascular endothelial growth factor
positively correlated with prostate cancer clinical increased N-cadherin and enhanced vimentin staining.
risk and suggests that it is a stronger predictor of The authors additionally provide evidence that these
Gleason score than serum PSA. Endo180 disrupts effects are mediated via FAK-Src signalling.
epithelial cell contact and plays a potential role in
EMT in prostate cancer. Endo180 and MT1-MMP co- A study by Sankpal et al. [37] provides evidence for
expression was identified as strongly upregulated regulation of MT1-MMP by specificity protein 1 (Sp1).
in the stroma of prostate cancer with low clinical Sp1 is expressed in a number of different cancers, and
risk, indicating that tumor-associated stromal plays key regulatory roles in processes associated
fibroblasts can acquire the ability for effective collagen with prostate cancer progression and metastasis.
degradation and internalisation at the early stages of DU-145 cells were reported to express constitutively
tumor development. These findings are interesting phosphorylated ERK, while PC3 and PC3N cells
and add further support to prostate cancer cells express constitutively phosphorylated AKT/PKB and
influencing MT1-MMP expression in their surrounding c-Jun NH2 terminal kinase (JNK). Interestingly, both
microenvironment. MT1-MMP and Sp1 levels were decreased in PC3 cells
when PI3K and JNK were inhibited, and MT1-MMP
The transcription factor p53 is known to play significant levels were decreased in DU-145 cells when MEK
roles as a tumor suppressor in cancer progression. was inhibited. These results suggest Sp1-mediated
Wang et al. [36] considered the involvement of p53 in transcriptional regulation of MT1-MMP in prostate
prostate cancer cell invasion and metastasis, using cancer cell lines via differential signalling control [13,37] .
DU145 cells in which p53 was silenced by siRNA. Sroka et al. [25] additionally considered the relationship
Increased invasion and metastasis were observed in between IGF-1R and MT1-MMP in prostate cancer
a series of in vitro experiments, including increased cells and tissues, the expression data for which were
MT1-MMP expression and activity, along with that discussed earlier. IGF-1R has been identified to play a
of MMP-2 and MMP-9. These findings are also role in prostate cancer metastatic progression, through
consistent with the studies associating MT1-MMP PI3K, MAP kinase and ERK signalling [38] . Interestingly,
with EMT, as demonstrated by reduced E-cadherin, decreased MT1-MMP expression at mRNA and
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ December 12, 2017 319