Page 102 - Read Online
P. 102
Falconer et al. MT-MMPs in prostate cancer
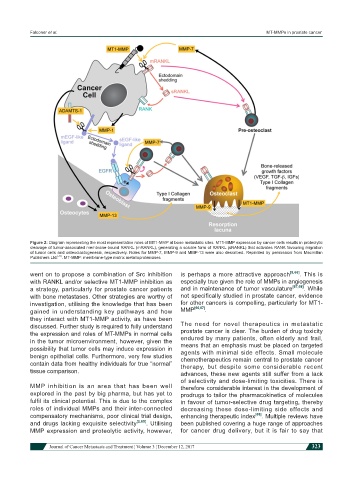
Figure 2: Diagram representing the most representative roles of MT1-MMP at bone metastatic sites. MT1-MMP expression by cancer cells results in proteolytic
cleavage of tumor-associated membrane-bound RANKL (mRANKL), generating a soluble form of RANKL (sRANKL) that activates RANK favouring migration
of tumor cells and osteoclastogenesis, respectively. Roles for MMP-7, MMP-9 and MMP-13 were also described. Reprinted by permission from Macmillan
[78]
Publishers Ltd. . MT-MMP: membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases
went on to propose a combination of Src inhibition is perhaps a more attractive approach [5,66] . This is
with RANKL and/or selective MT1-MMP inhibition as especially true given the role of MMPs in angiogenesis
a strategy, particularly for prostate cancer patients and in maintenance of tumor vasculature [67,68] . While
with bone metastases. Other strategies are worthy of not specifically studied in prostate cancer, evidence
investigation, utilising the knowledge that has been for other cancers is compelling, particularly for MT1-
gained in understanding key pathways and how MMP [66,67] .
they interact with MT1-MMP activity, as have been
discussed. Further study is required to fully understand The need for novel therapeutics in metastatic
the expression and roles of MT-MMPs in normal cells prostate cancer is clear. The burden of drug toxicity
in the tumor microenvironment, however, given the endured by many patients, often elderly and frail,
possibility that tumor cells may induce expression in means that an emphasis must be placed on targeted
benign epithelial cells. Furthermore, very few studies agents with minimal side effects. Small molecule
chemotherapeutics remain central to prostate cancer
contain data from healthy individuals for true “normal” therapy, but despite some considerable recent
tissue comparison. advances, these new agents still suffer from a lack
of selectivity and dose-limiting toxicities. There is
MMP inhibition is an area that has been well therefore considerable interest in the development of
explored in the past by big pharma, but has yet to prodrugs to tailor the pharmacokinetics of molecules
fulfil its clinical potential. This is due to the complex in favour of tumor-selective drug targeting, thereby
roles of individual MMPs and their inter-connected decreasing these dose-limiting side effects and
compensatory mechanisms, poor clinical trial design, enhancing therapeutic index [69] . Multiple reviews have
and drugs lacking exquisite selectivity [2,65] . Utilising been published covering a huge range of approaches
MMP expression and proteolytic activity, however, for cancer drug delivery, but it is fair to say that
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ December 12, 2017 323