Page 69 - Read Online
P. 69
Pippione et al. Steroidogenic enzymes in prostate cancer
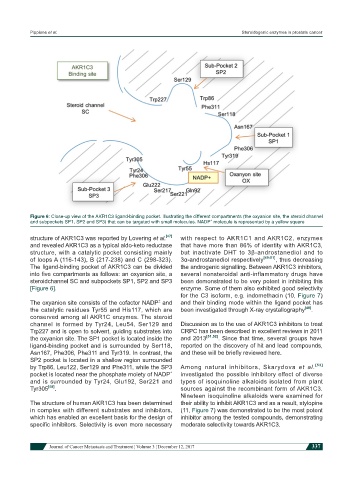
Figure 6: Close-up view of the AKR1C3 ligand-binding pocket. Illustrating the different compartments (the oxyanion site, the steroid channel
+
and subpockets SP1, SP2 and SP3) that can be targeted with small molecules. NADP molecule is represented by a yellow square
structure of AKR1C3 was reported by Lovering et al. [47] with respect to AKR1C1 and AKR1C2, enzymes
and revealed AKR1C3 as a typical aldo-keto reductase that have more than 86% of identity with AKR1C3,
structure, with a catalytic pocket consisting mainly but inactivate DHT to 3β-androstanediol and to
of loops A (116-143), B (217-238) and C (298-323). 3α-androstanediol respectively [49-51] , thus decreasing
The ligand-binding pocket of AKR1C3 can be divided the androgenic signalling. Between AKR1C3 inhibitors,
into five compartments as follows: an oxyanion site, a several nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have
steroidchannel SC and subpockets SP1, SP2 and SP3 been demonstrated to be very potent in inhibiting this
[Figure 6]. enzyme. Some of them also exhibited good selectivity
for the C3 isoform, e.g. indomethacin (10, Figure 7)
+
The oxyanion site consists of the cofactor NADP and and their binding mode within the ligand pocket has
the catalytic residues Tyr55 and His117, which are been investigated through X-ray crystallography [48] .
conserved among all AKR1C enzymes. The steroid
channel is formed by Tyr24, Leu54, Ser129 and Discussion as to the use of AKR1C3 inhibitors to treat
Trp227 and is open to solvent, guiding substrates into CRPC has been described in excellent reviews in 2011
the oxyanion site. The SP1 pocket is located inside the and 2013 [51,52] . Since that time, several groups have
ligand-binding pocket and is surrounded by Ser118, reported on the discovery of hit and lead compounds,
Asn167, Phe306, Phe311 and Tyr319. In contrast, the and these will be briefly reviewed here.
SP2 pocket is located in a shallow region surrounded
by Trp86, Leu122, Ser129 and Phe311, while the SP3 Among natural inhibitors, Skarydova et al. [53]
+
pocket is located near the phosphate moiety of NADP investigated the possible inhibitory effect of diverse
and is surrounded by Tyr24, Glu192, Ser221 and types of isoquinoline alkaloids isolated from plant
Tyr305 [48] . sources against the recombinant form of AKR1C3.
Nineteen isoquinoline alkaloids were examined for
The structure of human AKR1C3 has been determined their ability to inhibit AKR1C3 and as a result, stylopine
in complex with different substrates and inhibitors, (11, Figure 7) was demonstrated to be the most potent
which has enabled an excellent basis for the design of inhibitor among the tested compounds, demonstrating
specific inhibitors. Selectivity is even more necessary moderate selectivity towards AKR1C3.
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ December 12, 2017 337