Page 40 - Read Online
P. 40
Terai et al. The liver and metastatic uveal melanoma
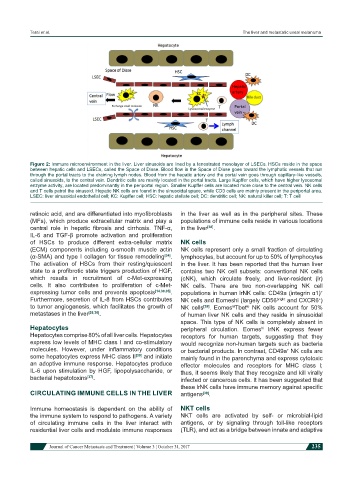
Figure 2: Immune microenvironment in the liver. Liver sinusoids are lined by a fenestrated monolayer of LSECs. HSCs reside in the space
between hepatic cells and LSECs, called the Space of Disse. Blood flow in the Space of Disse goes toward the lymphatic vessels that run
through the portal tracts to the draining lymph nodes. Blood from the hepatic artery and the portal vein goes through capillary-like vessels,
called sinusoids, to the central vein. Dendritic cells are mainly located in the portal tracts. Large Kupffer cells, which have higher lysosomal
enzyme activity, are located predominantly in the periportal region. Smaller Kupffer cells are located more close to the central vein. NK cells
and T cells patrol the sinusoid. Hepatic NK cells are found in the sinusoidal space, while CD3 cells are mainly present in the periportal area.
LSEC: liver sinusoidal endothelial cell; KC: Kupffer cell; HSC: hepatic stellate cell; DC: dendritic cell; NK: natural killer cell; T: T cell
retinoic acid, and are differentiated into myofibroblasts in the liver as well as in the peripheral sites. These
(MFs), which produce extracellular matrix and play a populations of immune cells reside in various locations
central role in hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis. TNF-α, in the liver [38] .
IL-6 and TGF-β promote activation and proliferation
of HSCs to produce different extra-cellular matrix NK cells
(ECM) components including α-smooth muscle actin NK cells represent only a small fraction of circulating
(α-SMA) and type I collagen for tissue remodeling [34] . lymphocytes, but account for up to 50% of lymphocytes
The activation of HSCs from their resting/quiescent in the liver. It has been reported that the human liver
state to a profibrotic state triggers production of HGF, contains two NK cell subsets: conventional NK cells
which results in recruitment of c-Met-expressing (cNK), which circulate freely, and liver-resident (lr)
cells. It also contributes to proliferation of c-Met- NK cells. There are two non-overlapping NK cell
expressing tumor cells and prevents apoptosis [14,30,35] . populations in human lrNK cells: CD49a (integrin α1)
+
Furthermore, secretion of IL-8 from HSCs contributes NK cells and Eomeshi (largely CD56 bright and CXCR6 )
+
to tumor angiogenesis, which facilitates the growth of NK cells [39] . Eomes Tbet NK cells account for 50%
hi
lo
metastases in the liver [28,36] . of human liver NK cells and they reside in sinusoidal
space. This type of NK cells is completely absent in
Hepatocytes peripheral circulation. Eomes lrNK express fewer
hi
Hepatocytes comprise 80% of all liver cells. Hepatocytes receptors for human targets, suggesting that they
express low levels of MHC class I and co-stimulatory would recognize non-human targets such as bacteria
molecules. However, under inflammatory conditions or bacterial products. In contrast, CD49a NK cells are
+
some hepatocytes express MHC class II [30] and initiate mainly found in the parenchyma and express cytotoxic
an adoptive immune response. Hepatocytes produce effector molecules and receptors for MHC class I;
IL-6 upon stimulation by HGF, lipopolysaccharide, or thus, it seems likely that they recognize and kill virally
bacterial hepatotoxins [37] . infected or cancerous cells. It has been suggested that
these lrNK cells have immune memory against specific
CIRCULATING IMMUNE CELLS IN THE LIVER antigens [39] .
Immune homeostasis is dependent on the ability of NKT cells
the immune system to respond to pathogens. A variety NKT cells are activated by self- or microbial-lipid
of circulating immune cells in the liver interact with antigens, or by signaling through toll-like receptors
residential liver cells and modulate immune responses (TLR), and act as a bridge between innate and adaptive
Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ October 31, 2017 235