Page 39 - Read Online
P. 39
Terai et al. The liver and metastatic uveal melanoma
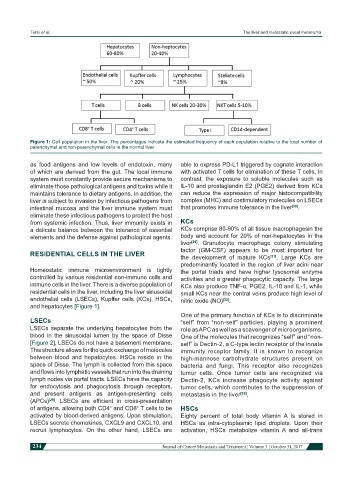
Figure 1: Cell population in the liver. The percentages indicate the estimated frequency of each population relative to the total number of
parenchymal and non-parenchymal cells in the normal liver
as food antigens and low levels of endotoxin, many able to express PD-L1 triggered by cognate interaction
of which are derived from the gut. The local immune with activated T cells for elimination of these T cells. In
system must constantly provide secure mechanisms to contrast, the exposure to soluble molecules such as
eliminate those pathological antigens and toxins while it IL-10 and prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) derived from KCs
maintains tolerance to dietary antigens. In addition, the can reduce the expression of major histocompatibility
liver is subject to invasion by infectious pathogens from complex (MHC) and costimulatory molecules on LSECs
intestinal mucosa and the liver immune system must that promotes immune tolerance in the liver [30] .
eliminate these infectious pathogens to protect the host
from systemic infection. Thus, liver immunity exists in KCs
a delicate balance between the tolerance of essential KCs comprise 80-90% of all tissue macrophagesin the
elements and the defense against pathological agents. body and account for 20% of non-hepatocytes in the
liver [29] . Granulocyte macrophage colony stimulating
factor (GM-CSF) appears to be most important for
RESIDENTIAL CELLS IN THE LIVER
the development of mature KCs [31] . Large KCs are
predominantly located in the region of liver acini near
Homeostatic immune microenvironment is tightly the portal triads and have higher lysosomal enzyme
controlled by various residential non-immune cells and activities and a greater phagocytic capacity. The large
immune cells in the liver. There is a diverse population of KCs also produce TNF-α, PGE2, IL-10 and IL-1, while
residential cells in the liver, including the liver sinusoidal small KCs near the central veins produce high level of
endothelial cells (LSECs), Kupffer cells (KCs), HSCs, nitric oxide (NO) [32] .
and hepatocytes [Figure 1].
One of the primary function of KCs is to discriminate
LSECs “self” from “non-self” particles, playing a prominent
LSECs separate the underlying hepatocytes from the role as APC as well as a scavenger of microorganisms.
blood in the sinusoidal lumen by the space of Disse One of the molecules that recognizes “self” and “non-
[Figure 2]. LSECs do not have a basement membrane. self” is Dectin-2, a C-type lectin receptor of the innate
This structure allows for the quick exchange of molecules immunity receptor family. It is known to recognize
between blood and hepatocytes. HSCs reside in the high-mannose carbohydrate structures present on
space of Disse. The lymph is collected from this space bacteria and fungi. This receptor also recognizes
and flows into lymphatic vessels that run into the draining tumor cells. Once tumor cells are recognized via
lymph nodes via portal tracts. LSECs have the capacity Dectin-2, KCs increase phagocyte activity against
for endocytosis and phagocytosis through receptors, tumor cells, which contributes to the suppression of
and present antigens as antigen-presenting cells metastasis in the liver [33] .
(APCs) [29] . LSECs are efficient in cross-presentation
of antigens, allowing both CD4 and CD8 T cells to be HSCs
+
+
activated by blood-derived antigens. Upon stimulation, Eighty percent of total body vitamin A is stored in
LSECs secrete chemokines, CXCL9 and CXCL10, and HSCs as intra-cytoplasmic lipid droplets. Upon their
recruit lymphocytes. On the other hand, LSECs are activation, HSCs metabolize vitamin A and all-trans
234 Journal of Cancer Metastasis and Treatment ¦ Volume 3 ¦ October 31, 2017