Page 35 - Read Online
P. 35
Ayass et al. Intell Robot 2022;2(1):20-36 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2021.07 Page 30
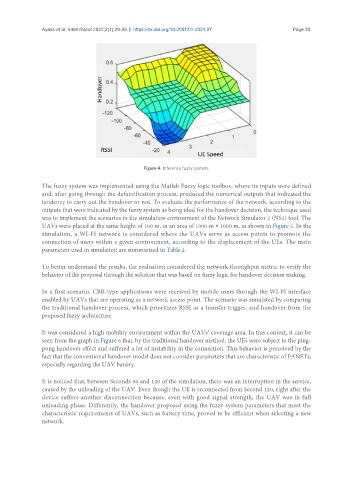
Figure 4. Inference fuzzy system.
The fuzzy system was implemented using the Matlab Fuzzy logic toolbox, where its inputs were defined
and, after going through the defuzzification process, produced the numerical outputs that indicated the
tendency to carry out the handover or not. To evaluate the performance of the network, according to the
outputs that were indicated by the fuzzy system as being ideal for the handover decision, the technique used
was to implement the scenarios in the simulation environment of the Network Simulator 2 (NS2) tool. The
UAVs were placed at the same height of 100 m, in an area of 1000 m × 1000 m, as shown in Figure 5. In the
simulation, a WI-FI network is considered where the UAVs serve as access points to promote the
connection of users within a given environment, according to the displacement of the UEs. The main
parameters used in simulation are summarized in Table 2.
To better understand the results, the evaluation considered the network throughput metric to verify the
behavior of the proposal through the solution that was based on fuzzy logic for handover decision making.
In a first scenario, CBR-type applications were received by mobile users through the WI-FI interface
enabled by UAVs that are operating as a network access point. The scenario was simulated by comparing
the traditional handover process, which prioritizes RSSI as a transfer trigger, and handover from the
proposed fuzzy architecture.
It was considered a high mobility environment within the UAVs’ coverage area. In this context, it can be
seen from the graph in Figure 6 that, by the traditional handover method, the UEs were subject to the ping-
pong handover effect and suffered a lot of instability in the connection. This behavior is perceived by the
fact that the conventional handover model does not consider parameters that are characteristic of FANETs,
especially regarding the UAV battery.
It is noticed that, between Seconds 90 and 120 of the simulation, there was an interruption in the service,
caused by the unloading of the UAV. Even though the UE is reconnected from Second 120, right after the
device suffers another disconnection because, even with good signal strength, the UAV was in full
unloading phase. Differently, the handover proposed using the fuzzy system parameters that meet the
characteristic requirements of UAVs, such as battery time, proved to be efficient when selecting a new
network.