Page 47 - Read Online
P. 47
Page 516 Liu et al. Intell Robot 2024;4(4):503-23 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2024.29
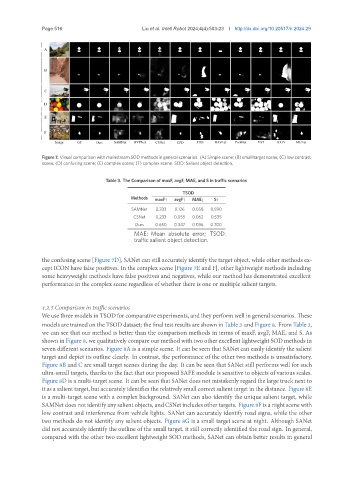
Figure 7. Visual comparison with mainstream SOD methods in general scenarios. (A) Simple scene; (B) small target scene; (C) low contrast
scene; (D) confusing scene; (E) complex scene; (F) complex scene. SOD: Salient object detection.
Table 3. The Comparison of maxF, avgF, MAE, and S in traffic scenarios
TSOD
Methods
maxF↑ avgF↑ MAE↓ S↑
SAMNet 0.333 0.126 0.058 0.590
CSNet 0.233 0.055 0.062 0.535
Ours 0.650 0.347 0.036 0.700
MAE: Mean absolute error; TSOD:
traffic salient object detection.
the confusing scene [Figure 7D], SANet can still accurately identify the target object, while other methods ex-
cept ICON have false positives. In the complex scene [Figure 7E and F], other lightweight methods including
some heavyweight methods have false positives and negatives, while our method has demonstrated excellent
performance in the complex scene regardless of whether there is one or multiple salient targets.
4.2.5 Comparison in traffic scenarios
We use three models in TSOD for comparative experiments, and they perform well in general scenarios. These
models are trained on the TSOD dataset; the final test results are shown in Table 3 and Figure 8. From Table 3,
we can see that our method is better than the comparison methods in terms of maxF, avgF, MAE, and S. As
shown in Figure 8, we qualitatively compare our method with two other excellent lightweight SOD methods in
seven different scenarios. Figure 8A is a simple scene. It can be seen that SANet can easily identify the salient
target and depict its outline clearly. In contrast, the performance of the other two methods is unsatisfactory.
Figure 8B and C are small target scenes during the day. It can be seen that SANet still performs well for such
ultra-small targets, thanks to the fact that our proposed SAFE module is sensitive to objects of various scales.
Figure 8D is a multi-target scene. It can be seen that SANet does not mistakenly regard the large truck next to
it as a salient target, but accurately identifies the relatively small correct salient target in the distance. Figure 8E
is a multi-target scene with a complex background. SANet can also identify the unique salient target, while
SAMNet does notidentify any salient objects, and CSNet includes other targets. Figure 8F is a night scene with
low contrast and interference from vehicle lights. SANet can accurately identify road signs, while the other
two methods do not identify any salient objects. Figure 8G is a small target scene at night. Although SANet
did not accurately identify the outline of the small target, it still correctly identified the road sign. In general,
compared with the other two excellent lightweight SOD methods, SANet can obtain better results in general