Page 173 - Read Online
P. 173
Page 233 Li et al. Intell Robot 2024;4(3):230-43 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/ir.2024.15
Hidden state
Ht-1 Ht
1-
Rt Zt Candidate
σ σ tanh …… Hidden state
~
Ht
Input Xt
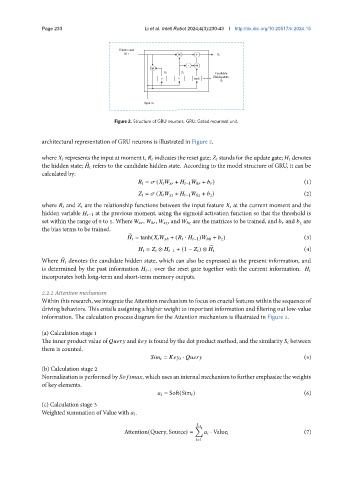
Figure 2. Structure of GRU neurons. GRU: Gated recurrent unit.
architectural representation of GRU neurons is illustrated in Figure 2.
where represents the input at moment t, indicates the reset gate; stands for the update gate; denotes
the hidden state; refers to the candidate hidden state. According to the model structure of GRU, it can be
˜
calculated by:
= ( + −1 ℎ + ) (1)
= ( + −1 ℎ + ) (2)
where and are the relationship functions between the input feature at the current moment and the
hidden variable −1 at the previous moment, using the sigmoid activation function so that the threshold is
set within the range of 0 to 1. Where , ℎ , , and ℎ are the matrices to be trained, and and are
the bias terms to be trained.
e
= tanh( ℎ + ( · −1 ) ℎℎ + ) (3)
e
= ⊗ −1 + (1 − ) ⊗ (4)
Where denotes the candidate hidden state, which can also be expressed as the present information, and
˜
is determined by the past information −1 over the reset gate together with the current information.
incorporates both long-term and short-term memory outputs.
2.2.2 Attention mechanism
Within this research, we integrate the Attention mechanism to focus on crucial features within the sequence of
driving behaviors. This entails assigning a higher weight to important information and filtering out low-value
information. The calculation process diagram for the Attention mechanism is illustrated in Figure 3.
(a) Calculation stage 1
The inner product value of and is found by the dot product method, and the similarity between
them is counted.
= · (5)
(b) Calculation stage 2
Normalization is performed by , which uses an internal mechanism to further emphasize the weights
of key elements.
= Soft(Sim ) (6)
(c) Calculation stage 3
Weighted summation of Value with .
Õ
Attention(Query,Source) = · Value (7)
=1