Page 496 - Read Online
P. 496
Zeng et al. Hepatoma Res2020;6:43 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.29 Page 3 of 12
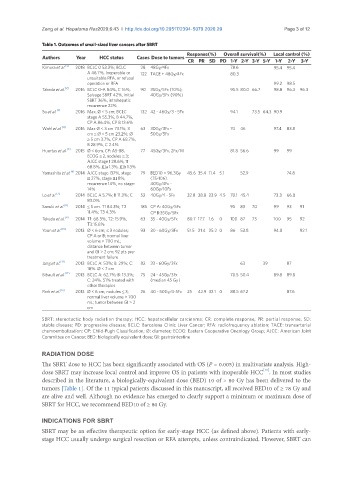
Table 1. Outcomes of small-sized liver cancers after SBRT
Response(%) Overall survival(%) Local control (%)
Authors Year HCC status Cases Dose to tumors
CR PR SD PD 1-Y 2-Y 3-Y 5-Y 1-Y 2-Y 3-Y
Kimura et al. [1] 2018 BCLC 0 53.3%; BCLC 28 48Gy/4Fx 78.6 95.4 95.4
A 46.7%, Inoperable or 122 TACE + 48Gy/4Fx 80.3
unsuitable RFA, or refusal
operation or RFA 99.2 98.5
Takeda et al. [2] 2016 BCLC 0-A 84%, C 16%, 90 35Gy/5Fx (10%); 95.5 80.0 66.7 98.8 96.3 96.3
Salvage SBRT 42%, initial 40Gy/5Fx (90%)
SBRT 36%, intrahepatic
recurrence 22%
Su et al. [3] 2016 Max. Ø ≤ 5 cm; BCLC 132 42 - 46Gy/3 - 5Fx 94.1 73.5 64.3 90.9
stage A 55.3%, B 44.7%,
CP A 86.4%, CP B 13.6%
Wahl et al. [4] 2016 Max Ø < 3 cm 73.1%; 3 63 30Gy/3Fx - 74 46 97.4 83.8
cm ≤ Ø < 5 cm 23.2%; Ø 50Gy/5Fx
≥ 5 cm 3.7%, CP A 68.7%,
B 28.9%, C 2.4%
Huertas et al. [5] 2015 Ø ≤ 6cm, CP: A5-B8, 77 45Gy/3Fx, 2Fx/W 81.8 56.6 99 99
ECOG ≤ 2, nodules ≤ 3;
AJCC stage I 28.6%, II
68.8%, IIIa 1.3%, IIIb 1.3%
Yamashita et al. [6] 2014 AJCC stage I37%, stage 79 BED10 = 96.3Gy 45.6 35.4 11.4 5.1 52.9 74.8
II 27%, stage III 8%, (75-106).
recurrence 14%, no stage: 40Gy/4Fx -
14% 60Gy/10Fx
Lo et al. [7] 2014 BCLC A 5.7%; B 11.3%; C 53 40Gy/4 - 5Fx 32.8 38.8 23.9 4.5 70.1 45.4 73.3 66.8
83.0%
Sanuki et al. [8] 2014 ≤ 5 cm. T1 84.3%; T2 185 CP A: 40Gy/5Fx 95 83 70 99 93 91
11.4%; T3 4.3% CP B:35Gy/5Fx
Tekeda et al. [9] 2014 T1: 68.3%, T2: 15.9%, 63 35 - 40Gy/5Fx 80.7 17.7 1.6 0 100 87 73 100 95 92
T3:15.8%
Yoon et al. [10] 2013 Ø < 6 cm; ≤ 3 nodules; 93 30 - 60Gy/3Fx 51.5 21.4 25.2 0 86 53.8 94.8 92.1
CP A or B; normal liver
volume > 700 mL;
distance between tumor
and GI > 2 cm; 92 pts pre-
treatment failure
Jang et al. [11] 2013 BCLC A: 53%; B: 29%; C: 82 33 - 60Gy/3Fx 63 39 87
18%. Ø < 7 cm
Bibault et al. [12] 2013 BCLC A: 62.7%; B: 13.3%; 75 24 - 45Gy/3Fx 78.5 50.4 89.8 89.8
C: 24%. 51% treated with (median 45 Gy)
other therapies
Park et al. [13] 2013 Ø < 6 cm; nodules ≤ 3; 26 40 - 50Gy/4-5Fx 25 42.9 32.1 0 88.5 67.2 87.6
normal liver volume > 700
mL; tumor between GI > 2
cm
SBRT: stereotactic body radiation therapy; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma; CR: complete response; PR: partial response; SD:
stable disease; PD: progressive disease; BCLC: Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer; RFA: radiofrequency ablation; TACE: transarterial
chemoembolization; CP: Child-Pugh Classification; Ø: diameter; ECOG: Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group; AJCC: American Joint
Committee on Cancer; BED: biologically equivalent dose; GI: gastrointestine
RADIATION DOSE
The SBRT dose to HCC has been significantly associated with OS (P = 0.005) in multivariate analysis. High-
[11]
dose SBRT may increase local control and improve OS in patients with inoperable HCC . In most studies
described in the literature, a biologically-equivalent dose (BED) 10 of > 80 Gy has been delivered to the
tumors [Table 1]. Of the 11 typical patients discussed in this manuscript, all received BED10 of ≥ 78 Gy and
are alive and well. Although no evidence has emerged to clearly support a minimum or maximum dose of
SBRT for HCC, we recommend BED10 of ≥ 80 Gy.
INDICATIONS FOR SBRT
SBRT may be an effective therapeutic option for early-stage HCC (as defined above). Patients with early-
stage HCC usually undergo surgical resection or RFA attempts, unless contraindicated. However, SBRT can