Page 47 - Read Online
P. 47
Della Porta et al. Comparison of p53 and prohibitin expression
proinflammatory stimuli can be responsible for NFκB NFκB leads to infected hepatocytes survival and
activation, which results in protection of hepatocytes consequent HCV infection persistence. [21]
[9]
from apoptosis. Moreover, the HCV core protein
potentiates NFκB activation and chronically activated In the present study, RelA/p65 nuclear labelling
P53 labeling score Cytoplasmic PHB labeling score Nuclear PHB labeling score
TUNEL labeling (%)
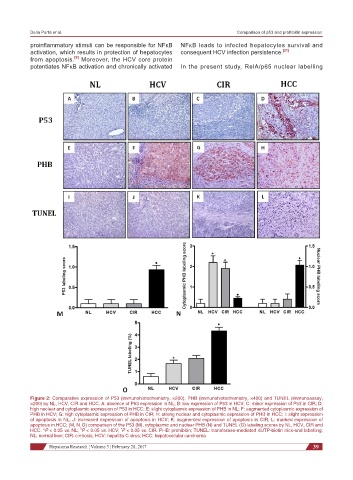
Figure 2: Comparative expression of P53 (immunohistochemistry, ×200), PHB (immunohistochemistry, ×400) and TUNEL (immunoassay,
×200) by NL, HCV, CIR and HCC. A: absence of P53 expression in NL; B: low expression of P53 in HCV; C: minor expression of P53 in CIR; D:
high nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of P53 in HCC; E: slight cytoplasmic expression of PHB in NL; F: augmented cytoplasmic expression of
PHB in HCV; G: high cytoplasmic expression of PHB in CIR; H: strong nuclear and cytoplasmic expression of PHB in HCC; I: slight expression
of apoptosis in NL; J: increased expression of apoptosis in HCV; K: augmented expression of apoptosis in CIR; L: marked expression of
apoptosis in HCC; (M, N, O) comparison of the P53 (M), cytoplasmic and nuclear PHB (N) and TUNEL (O) labeling scores by NL, HCV, CIR and
0
•
HCC. *P < 0.05 vs. NL; P < 0.05 vs. HCV; P < 0.05 vs. CIR. PHB: prohibitin; TUNEL: transferase-mediated dUTP-biotin nick-end labelling;
NL: normal liver; CIR: cirrhosis; HCV: hepatitis C virus; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ February 28, 2017 39