Page 46 - Read Online
P. 46
Della Porta et al. Comparison of p53 and prohibitin expression
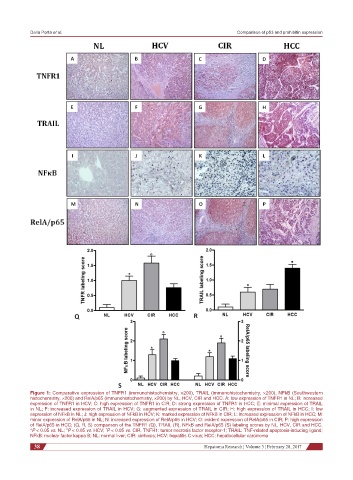
Figure 1: Comparative expression of TNFR1 (immunohistochemistry, ×200), TRAIL (immunohistochemistry, ×200), NFkB (Southwestern
histochemistry, ×200) and RelA/p65 (immunohistochemistry, ×200) by NL, HCV, CIR and HCC. A: low expression of TNFR1 in NL; B: increased
expression of TNFR1 in HCV; C: high expression of TNFR1 in CIR; D: strong expression of TNFR1 in HCC; E: minimal expression of TRAIL
in NL; F: increased expression of TRAIL in HCV; G: augmented expression of TRAIL in CIR; H: high expression of TRAIL in HCC; I: low
expression of NFkB in NL; J: high expression of NFkB in HCV; K: marked expression of NFkB in CIR; L: increased expression of NFkB in HCC; M:
minor expression of RelA/p65 in NL; N: increased expression of RelA/p65 in HCV; O: evident expression of RelA/p65 in CIR; P: high expression
of RelA/p65 in HCC; (Q, R, S) comparison of the TNFR1 (Q), TRAIL (R), NFkB and RelA/p65 (S) labeling scores by NL, HCV, CIR and HCC.
0
•
*P < 0.05 vs. NL; P < 0.05 vs. HCV; P < 0.05 vs. CIR. TNFR1: tumor necrosis factor receptor-1; TRAIL: TNF-related apoptosis-inducing ligand;
NFkB: nuclear factor kappa B; NL: normal liver; CIR: cirrhosis; HCV: hepatitis C virus; HCC: hepatocellular carcinoma
38 Hepatoma Research ¦ Volume 3 ¦ February 28, 2017