Page 244 - Read Online
P. 244
In our examination, there was increased identification
A B
of feeding arteries associated with HCC in the right and
caudate hepatic lobes. CBCT imaging is also reported to be
useful for detecting HCC of approximately 1 cm in size that
were unidentified following DSA imaging. CBCT imaging is
considered desirable in such cases.
Advances in technology will simplify CBCT imaging,
reduce radiation exposure, and process images faster.
If all three-dimensional imaging becomes possible,
C D then three-dimensional treatment using CBCT imaging
is expected to become routine practice, replacing the
traditional two-dimensional treatment procedure in
endovascular intervention for HCC. [23]
There are some limitations in this study. First, the field of
view by CBCT was narrower than DSA. Therefore, CBCT is
unable to obtain a complete liver image in some cases. We
should set the field of view around the region of interest in
the liver. Next, we defined HCC as vascular enhancement
E F on DSA imaging after superselective catheterization
and nodular deposition of Lipiodol on CT imaging after
treatment. There were no residual HCCs on CT performed
two-weeks after treatment. However, we cannot exclude
the possibility of very small residual HCCs. Moreover, we did
not evaluate the specificity of detection of HCC nodules and
their feeding arteries.
In this study, adding CBCT imaging to conventional two-
dimensional DSA imaging increased the HCC detection
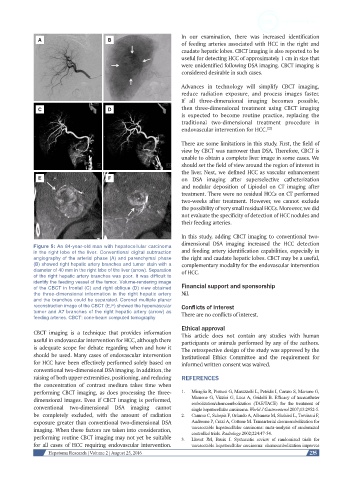
Figure 5: An 84-year-old man with hepatocellular carcinoma
in the right lobe of the liver. Conventional digital subtraction and feeding artery identification capabilities, especially in
angiography of the arterial phase (A) and parenchymal phase the right and caudate hepatic lobes. CBCT may be a useful,
(B) showed right hepatic artery branches and tumor stain with a complementary modality for the endovascular intervention
diameter of 40 mm in the right lobe of the liver (arrow). Separation of HCC.
of the right hepatic artery branches was poor. It was difficult to
identify the feeding vessel of the tumor. Volume-rendering image
of the CBCT in frontal (C) and right oblique (D) view obtained Financial support and sponsorship
the three-dimensional information in the right hepatic artery Nil.
and the branches could be separated. Coronal multiple planar
reconstruction image of the CBCT (E,F) showed the hypervascular Conflicts of interest
tumor and A7 branches of the right hepatic artery (arrow) as There are no conflicts of interest.
feeding arteries. CBCT: cone-beam computed tomography
Ethical approval
CBCT imaging is a technique that provides information This article does not contain any studies with human
useful in endovascular intervention for HCC, although there participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
is adequate scope for debate regarding when and how it The retrospective design of the study was approved by the
should be used. Many cases of endovascular intervention Institutional Ethics Committee and the requirement for
for HCC have been effectively performed solely based on informed written consent was waived.
conventional two-dimensional DSA imaging. In addition, the
raising of both upper extremities, positioning, and reducing REFERENCES
the concentration of contrast medium takes time when
performing CBCT imaging, as does processing the three- 1. Miraglia R, Pietrosi G, Maruzzelli L, Petridis I, Caruso S, Marrone G,
dimensional images. Even if CBCT imaging is performed, Mamone G, Vizzini G, Luca A, Gridelli B. Efficacy of transcatheter
embolization/chemoembolization (TAE/TACE) for the treatment of
conventional two-dimensional DSA imaging cannot single hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2007;13:2952-5.
be completely excluded, with the amount of radiation 2. Camma C, Schepis F, Orlando A, Albanese M, Shahied L, Trevisani F,
exposure greater than conventional two-dimensional DSA Andreone P, Craxì A, Cottone M. Transarterial chemoembolization for
imaging. When these factors are taken into consideration, unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: meta-analysis of randomized
controlled trials. Radiology 2002;224:47-54.
performing routine CBCT imaging may not yet be suitable 3. Llovet JM, Bruix J. Systematic review of randomized trials for
for all cases of HCC requiring endovascular intervention. unresectable hepatocellular carcinoma: chemoembolization improves
Hepatoma Research | Volume 2 | August 25, 2016 235