Page 148 - Read Online
P. 148
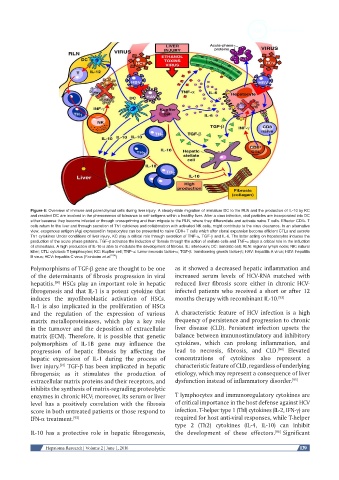
Figure 6: Overview of immune and parenchymal cells during liver injury. A steady-state migration of immature DC to the RLN and the production of IL-10 by KC
and resident DC are involved in the phenomenon of tolerance to self-antigens within a healthy liver. After a virus infection, viral particles are incorporated into DC
either because they become infected or through cross-priming and then migrate to the RLN, where they differentiate and activate naive T cells. Effector CD4+ T
cells return to the liver and through secretion of Th1 cytokines and collaboration with activated NK cells, might contribute to the virus clearance. In an alternative
view, exogenous antigen (Ag) expressed in hepatocytes can be presented to naive CD8+ T cells which after clonal expansion become efficient CTLs and secrete
Th1 cytokines Under conditions of liver injury, KC play a critical role through secretion of TNF-α, TGF-β and IL-6. The latter acting on hepatocytes induces the
production of the acute phase proteins. TGF-β activates the induction of fibrosis through the action of stellate cells and TNF-α plays a critical role in the induction
of cholestasis. A high production of IL-10 is able to modulate the development of fibrosis. IL: interleukin; DC: dendritic cell; RLN: regional lymph node; NK: natural
killer; CTL: cytotoxic T lymphocytes; KC: Kupffer cell; TNF-α: tumor necrosis factor-α; TGF-β: transforming growth factor-β; HAV: hepatitis A virus; HBV: hepatitis
B virus; HCV: hepatitis C virus (Fainboim et al. [104] )
Polymorphisms of TGF-β gene are thought to be one as it showed a decreased hepatic inflammation and
of the determinants of fibrosis progression in viral increased serum levels of HCV-RNA matched with
hepatitis. HSCs play an important role in hepatic reduced liver fibrosis score either in chronic HCV-
[90]
fibrogenesis and that IL-1 is a potent cytokine that infected patients who received a short or after 12
induces the myofibroblastic activation of HSCs. months therapy with recombinant IL-10. [93]
IL-1 is also implicated in the proliferation of HSCs
and the regulation of the expression of various A characteristic feature of HCV infection is a high
matrix metalloproteinases, which play a key role frequency of persistence and progression to chronic
in the turnover and the deposition of extracellular liver disease (CLD). Persistent infection upsets the
matrix (ECM). Therefore, it is possible that genetic balance between immunostimulatory and inhibitory
polymorphism of IL-1B gene may influence the cytokines, which can prolong inflammation, and
[94]
progression of hepatic fibrosis by affecting the lead to necrosis, fibrosis, and CLD. Elevated
hepatic expression of IL-1 during the process of concentrations of cytokines also represent a
liver injury. TGF-β has been implicated in hepatic characteristic feature of CLD, regardless of underlying
[91]
fibrogensis; as it stimulates the production of etiology, which may represent a consequence of liver
extracellular matrix proteins and their receptors, and dysfunction instead of inflammatory disorder. [95]
inhibits the synthesis of matrix-regrading proteolytic
enzymes in chronic HCV; moreover, its serum or liver T lymphocytes and immunoregulatory cytokines are
level has a positively correlation with the fibrosis of critical importance in the host defense against HCV
score in both untreated patients or those respond to infection. T-helper type 1 (Thl) cytokines (IL-2, IFN-γ) are
IFN-α treatment. [92] required for host anti-viral responses, while T-helper
type 2 (Th2) cytokines (IL-4, IL-10) can inhibit
IL-10 has a protective role in hepatic fibrogenesis, the development of these effectors. [96] Significant
Hepatoma Research | Volume 2 | June 1, 2016 139