Page 46 - Read Online
P. 46
Anugwom et al. Hepatoma Res 2022;8:7 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2021.123 Page 7 of 13
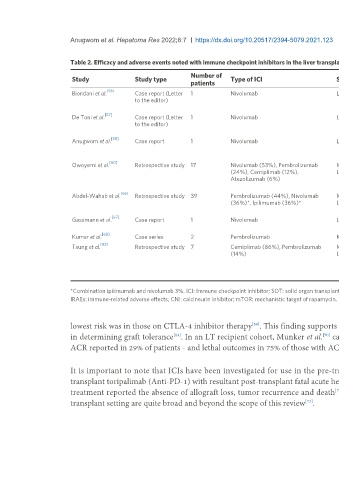
Table 2. Efficacy and adverse events noted with immune checkpoint inhibitors in the liver transplant recipient
Number of
Study Study type Type of ICI Sot type Major adverse findings
patients
[56]
Biondani et al. Case report (Letter 1 Nivolumab Liver transplant Patient had no adverse effects; suggesting that pre-emptive corticosteroids and the
to the editor) combination of tacrolimus and everolimus may have prevented hepatic immune-
related adverse events
[57]
De Toni et al. Case report (Letter 1 Nivolumab Liver transplant No adverse effects were seen suggesting that treatment with checkpoint inhibitors
to the editor) under close surveillance of liver function might be feasible in select transplant
recipients
[58]
Anugwom et al. Case report 1 Nivolumab Liver transplant Patient developed cholestatic disease in the allograft, with fatal confluent hepatic
necrosis, consequent synthetic dysfunction, severe esophagitis and gastrointestinal
hemorrhage
[60]
Owoyemi et al. Retrospective study 17 Nivolumab (53%), Pembrolizumab Mixed SOT (7 KT, 8 25% (2) of LT recipients suffered ACR
(24%), Cemiplimab (12%), LT, 2 OHT) 29% (2) of KT recipients had IRAEs (allograft rejection and colitis)
Atezolizumab (6%) One OHT recipient (50%) developed acute heart failure and died from presumed
nivolumab cardiotoxicity
[66]
Abdel-Wahab et al. Retrospective study 39 Pembrolizumab (44%), Nivolumab Mixed SOT 23 KT, 11 ACR seen in 49% KT recipients, 20% OHT recipients and 36% LT recipients
(36%)*, Ipilimumab (36%)* LT, 5 OHT Overall death in 46% of cases due to allograft rejection or rejection complication (4
KT, 3 LT, 1 OHT)
[67]
Gassmann et al. Case report 1 Nivolumab Liver transplant Severe cellular graft rejection, consequent decline in liver function and severe
coagulopathy and fatal intracranial hemorrhage.
[68]
Kumar et al. Case series 2 Pembrolizumab Kidney transplant Both patients developed acute cellular rejection, but grafts were salvaged
[83]
Tsung et al. Retrospective study 7 Cemiplimab (86%), Pembrolizumab Mixed SOT (4 KT, 2 1 (100%) lung transplant recipient developed steroid-responsive pneumonitis
(14%) LT, 1 lung transplant) 1 (25%) KT recipient developed progressive renal injury
Preserved allograft function and no adverse effects were seen in those (3 patients)
who received prophylactic steroids (all patients underwent minimization or
conversion of CNI to mTOR inhibitors)
*Combination ipilimumab and nivolumab 3%. ICI: Immune checkpoint inhibitor; SOT: solid organ transplant; KT: kidney transplant; LT: liver transplant; OHT: orthotopic heart transplant; ACR: acute cellular rejection;
IRAEs: immune-related adverse effects; CNI: calcineurin inhibitor; mTOR: mechanistic target of rapamycin.
lowest risk was in those on CTLA-4 inhibitor therapy . This finding supports the previously proposed theory that the PD-1 pathway could play a critical role
[68]
[69]
in determining graft tolerance . In an LT recipient cohort, Munker et al. carried out a systemic review of 14 cases of LT recipients treated with ICIs, with
[70]
ACR reported in 29% of patients - and lethal outcomes in 75% of those with ACR.
It is important to note that ICIs have been investigated for use in the pre-transplant setting, with mixed outcomes. One study reported the use of a pre-
transplant toripalimab (Anti-PD-1) with resultant post-transplant fatal acute hepatic necrosis . Another case series of nivolumab use for pre-transplant tumor
[71]
treatment reported the absence of allograft loss, tumor recurrence and death . Though this is worth mentioning, the safety and efficacy of ICIs in the pre-
[72]
transplant setting are quite broad and beyond the scope of this review .
[73]