Page 68 - Read Online
P. 68
Casolino et al. Hepatoma Res 2021;7:76 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2021.79 Page 11 of 23
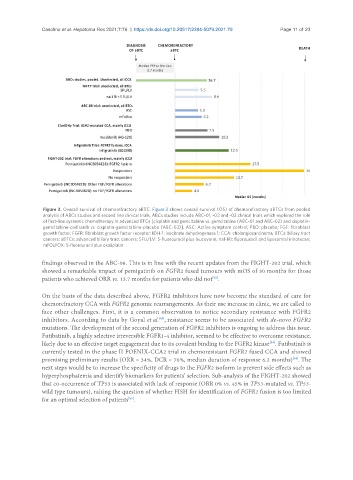
Figure 3. Overall survival of chemorefractory aBTC. Figure 3 shows overall survival (OS) of chemorefractory aBTCs from pooled
analysis of ABCs studies and second line clinical trials. ABCs studies include ABC-01, -02 and -03 clinical trials which explored the role
of first-line systemic chemotherapy in advanced BTCs [cisplatin and gemcitabine vs. gemcitabine (ABC-01 and ABC-02) and cisplatin-
gemcitabine-cediranib vs. cisplatin-gemcitabine-placebo (ABC-03)]. ASC: Active symptom control; PBO: placebo; FGF: fibroblast
growth factor; FGFR: fibroblast growth factor receptor; IDH-1: isocitrate dehydrogenase 1; CCA: cholangiocarcinoma; BTCs: biliary tract
cancers; aBTCs: advanced biliary tract cancers; 5FU/LV: 5-fluorouracil plus leucovorin; nal-IRI: fluorouracil and liposomial irinotecan;
mFOLFOX: 5-fluorouracil plus oxaliplatin.
findings observed in the ABC-06. This is in line with the recent updates from the FIGHT-202 trial, which
showed a remarkable impact of pemigatinib on FGFR2 fused tumours with mOS of 30 months for those
patients who achieved ORR vs. 13.7 months for patients who did not .
[82]
On the basis of the data described above, FGFR2 inhibitors have now become the standard of care for
chemorefractory CCA with FGFR2 genomic rearrangements. As their use increase in clinic, we are called to
face other challenges. First, it is a common observation to notice secondary resistance with FGFR2
inhibitors. According to data by Goyal et al. , resistance seems to be associated with de-novo FGFR2
[83]
mutations. The development of the second generation of FGFR2 inhibitors is ongoing to address this issue.
Futibatinib, a highly selective irreversible FGFR1-4 inhibitor, seemed to be effective to overcome resistance,
likely due to an effective target engagement due to its covalent binding to the FGFR2 kinase . Futibatinib is
[84]
currently tested in the phase II FOENIX-CCA2 trial in chemoresistant FGFR2 fused CCA and showed
promising preliminary results (ORR = 34%, DCR = 76%, median duration of response 6.2 months) . The
[84]
next steps would be to increase the specificity of drugs to the FGFR2 isoform to prevent side effects such as
hyperphosphatemia and identify biomarkers for patients’ selection. Sub-analysis of the FIGHT-202 showed
that co-occurrence of TP53 is associated with lack of response (ORR 0% vs. 45% in TP53-mutated vs. TP53-
wild type tumours), raising the question of whether FISH for identification of FGFR2 fusion is too limited
[85]
for an optimal selection of patients .