Page 64 - Read Online
P. 64
Casolino et al. Hepatoma Res 2021;7:76 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2021.79 Page 7 of 23
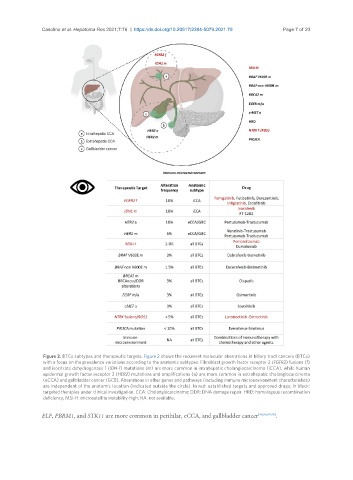
Figure 2. BTCs subtypes and therapeutic targets. Figure 2 shows the recurrent molecular aberrations in biliary tract cancers (BTCs)
with a focus on the prevalence variations according to the anatomic subtypes. Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (FGFR2) fusions (f)
and isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 (IDH-1) mutations (m) are more common in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma (iCCA), while human
epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) mutations and amplifications (a) are more common in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
(eCCA) and gallbladder cancer (GCB). Aberrations in other genes and pathways (including immune microenvironment characteristics)
are independent of the anatomic location (indicated outside the circle). In red: established targets and approved drugs; in black:
targeted therapies under clinical investigation. CCA: Cholangiocarcinoma; DDR: DNA damage repair. HRD: homologous recombination
deficiency; MSI-H: microsatellite instability-high; NA: not available.
ELF, PBRM1, and STK11 are more common in perihilar, eCCA, and gallbladder cancer [46,56,67,68] .