Page 73 - Read Online
P. 73
Page 16 of 23 Casolino et al. Hepatoma Res 2021;7:76 https://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2021.79
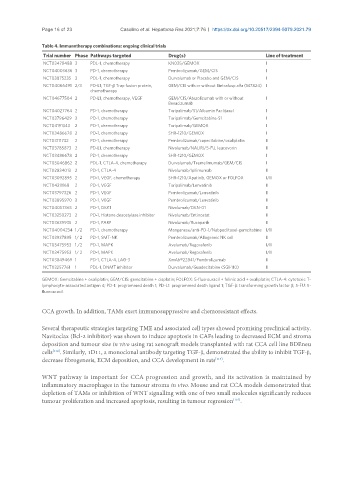
Table 4. Immunotherapy combinations: ongoing clinical trials
Trial number Phase Pathways targeted Drug(s) Line of treatment
NCT03478488 3 PDL-1, chemotherapy KN035/GEMOX I
NCT04003636 3 PD-1, chemotherapy Pembrolizumab/GEM/CIS I
NCT03875235 3 PDL-1, chemotherapy Durvalumab or Placebo and GEM/CIS I
NCT04066491 2/3 PD-L1; TGF-β Trap fusion protein, GEM/CIS with or without Bintrafusp alfa (M7824) I
chemotherapy
NCT04677504 2 PD-L1, chemotherapy, VEGF GEM/CIS/Atezolizumab with or without I
Bevacizumab
NCT04027764 2 PD-1, chemotherapy Toripalimab/S1/Albumin Paclitaxel I
NCT03796429 2 PD-1, chemotherapy Toripalimab/Gemcitabine-S1 I
NCT04191343 2 PD-1, chemotherapy Toripalimab/GEMOX I
NCT03486678 2 PD-1, chemotherapy SHR-1210/GEMOX I
NCT03111732 2 PD-1, chemotherapy Pembrolizumab/capecitabine/oxaliplatin II
NCT03785873 2 PD-L1, chemotherapy Nivolumab/NALIRI/5-FU, leucovorin II
NCT03486678 2 PD-1, chemotherapy SHR-1210/GEMOX I
NCT03046862 2 PDL-1, CTLA-4, chemotherapy Durvalumab/Tremelimumab/GEM/CIS I
NCT02834013 2 PD-1, CTLA-4 Nivolumab/Ipilimumab II
NCT03092895 2 PD-1, VEGF, chemotherapy SHR-1210/Apatinib, GEMOX or FOLFOX I/II
NCT04211168 2 PD-1, VEGF Toripalimab/Lenvatinib II
NCT03797326 2 PD-1, VEGF Pembrolizumab/Lenvatinib II
NCT03895970 2 PD-1, VEGF Pembrolizumab/Lenvatinib II
NCT04057365 2 PD-1, DKK1 Nivolumab/DKN-01 II
NCT03250273 2 PD-1, Histone deacetylase inhibitor Nivolumab/Entinostat II
NCT03639935 2 PD-1, PARP Nivolumab/Rucaparib II
NCT04004234 1 /2 PD-1, chemotherapy Manganese/anti-PD-1/Nabpaclitaxel-gemcitabine I/II
NCT03937895 1/ 2 PD-1, SMT-NK Pembrolizumab/Allogeneic NK cell II
NCT03475953 1 /2 PD-1, MAPK Avelumab/Regorafenib I/II
NCT03475953 1/ 2 PD-1, MAPK Avelumab/Regorafenib I/II
NCT03849469 1 PD-1, CTLA-4, LAG-3 XmAb®22841/Pembrolizumab II
NCT03257761 1 PDL-1, DNMT inhibitor Durvalumab/Guadecitabine (SGI-110) II
GEMOX: Gemcitabine + oxaliplatin; GEM/CIS: gemcitabine + cisplatin; FOLFOX: 5-fluorouracil + folinic acid + oxaliplatin; CTLA-4: cytotoxic T-
lymphocyte-associated antigen 4; PD-1: programmed death 1; PD-L1: programmed death ligand 1; TGF-β: transforming growth factor β; 5-FU: 5-
fluorouracil.
CCA growth. In addition, TAMs exert immunosuppressive and chemoresistant effects.
Several therapeutic strategies targeting TME and associated cell types showed promising preclinical activity.
Navitoclax (Bcl-2 inhibitor) was shown to induce apoptosis in CAFs leading to decreased ECM and stroma
deposition and tumour size in vivo using rat xenograft models transplanted with rat CCA cell line BDEneu
cells . Similarly, 1D11, a monoclonal antibody targeting TGF-β, demonstrated the ability to inhibit TGF-β,
[114]
decrease fibrogenesis, ECM deposition, and CCA development in rats .
[115]
WNT pathway is important for CCA progression and growth, and its activation is maintained by
inflammatory macrophages in the tumour stroma in vivo. Mouse and rat CCA models demonstrated that
depletion of TAMs or inhibition of WNT signalling with one of two small molecules significantly reduces
tumour proliferation and increased apoptosis, resulting in tumour regression .
[115]