Page 25 - Read Online
P. 25
Page 6 of 15 Feng et al. Hepatoma Res 2021;7:3 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.107
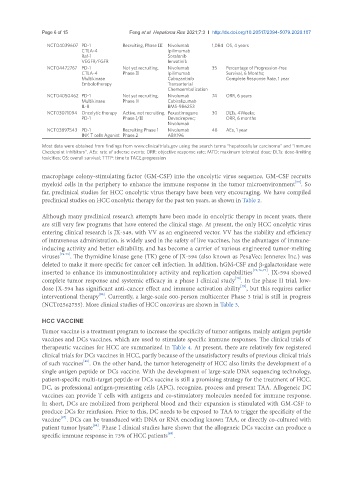
NCT04039607 PD-1 Recruiting, Phase III Nivolumab 1,084 OS, 4 years
CTLA-4 Ipilimumab
Raf-1 Sorafenib
VEGFR/FGFR lenvatinib
NCT04472767 PD-1 Not yet recruiting, Nivolumab 35 Percentage of Progression-free
CTLA-4 Phase II Ipilimumab Survival, 6 Months;
Multikinase Cabozantinib Complete Response Rate, 1 year
Embolotherapy Transarterial
Chemoembolization
NCT04050462 PD-1 Not yet recruiting, Nivolumab 74 ORR, 6 years
Multikinase Phase II Cabiralizumab
IL-8 BMS-986253
NCT03071094 Oncolytic therapy Active, not recruiting, Pexastimogene 30 DLTs, 4Weeks;
PD-1 Phase I/II Devacirepvec; ORR, 6 months
Nivolumab
NCT03897543 PD-1 Recruiting Phase 1 Nivolumab 48 AEs, 1 year
INK T cells Agonist Phase 2 ABX196
Most data were obtained from findings from www.clinicaltrials.gov using the search terms “hepatocellular carcinoma” and “Immune
Checkpoint Inhibitors”. AEs: rate of adverse events; ORR: objective response rate; MTD: maximum tolerated dose; DLTs: dose-limiting
toxicities; OS: overall survival; TTTP: time to TACE progression
macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF) into the oncolytic virus sequence, GM-CSF recruits
[53]
myeloid cells in the periphery to enhance the immune response in the tumor microenvironment . So
far, preclinical studies for HCC oncolytic virus therapy have been very encouraging. We have compiled
preclinical studies on HCC oncolytic therapy for the past ten years, as shown in Table 2.
Although many preclinical research attempts have been made in oncolytic therapy in recent years, there
are still very few programs that have entered the clinical stage. At present, the only HCC oncolytic virus
entering clinical research is JX-549, with VV as an engineered vector. VV has the stability and efficiency
of intravenous administration, is widely used in the safety of live vaccines, has the advantages of immune-
inducing activity and better editability, and has become a carrier of various engineered tumor-melting
viruses [73-75] . The thymidine kinase gene (TK) gene of JX-594 (also known as PexaVec; Jennerex Inc.) was
deleted to make it more specific for cancer cell infection. In addition, hGM-CSF and β-galactosidase were
inserted to enhance its immunostimulatory activity and replication capabilities [73,76,77] . JX-594 showed
complete tumor response and systemic efficacy in a phase I clinical study . In the phase II trial, low-
[78]
[79]
dose JX-594 has significant anti-cancer effect and immune activation ability , but this requires earlier
interventional therapy . Currently, a large-scale 600-person multicenter Phase 3 trial is still in progress
[80]
(NCT02562755). More clinical studies of HCC oncovirus are shown in Table 3.
HCC VACCINE
Tumor vaccine is a treatment program to increase the specificity of tumor antigens, mainly antigen peptide
vaccines and DCs vaccines, which are used to stimulate specific immune responses. The clinical trials of
therapeutic vaccines for HCC are summarized in Table 4. At present, there are relatively few registered
clinical trials for DCs vaccines in HCC, partly because of the unsatisfactory results of previous clinical trials
[86]
of such vaccines . On the other hand, the tumor heterogeneity of HCC also limits the development of a
single antigen peptide or DCs vaccine. With the development of large-scale DNA sequencing technology,
patient-specific multi-target peptide or DCs vaccine is still a promising strategy for the treatment of HCC.
DC, as professional antigen-presenting cells (APC), recognize, process and present TAA. Allogeneic DC
vaccines can provide T cells with antigens and co-stimulatory molecules needed for immune response.
In short, DCs are mobilized from peripheral blood and their expansion is stimulated with GM-CSF to
produce DCs for reinfusion. Prior to this, DC needs to be exposed to TAA to trigger the specificity of the
vaccine . DCs can be transduced with DNA or RNA encoding known TAA, or directly co-cultured with
[87]
[88]
patient tumor lysate . Phase I clinical studies have shown that the allogeneic DCs vaccine can produce a
[89]
specific immune response in 73% of HCC patients .