Page 79 - Read Online
P. 79
Ban et al. Hepatoma Res 2021;7:13 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.104 Page 5 of 8
A
B C
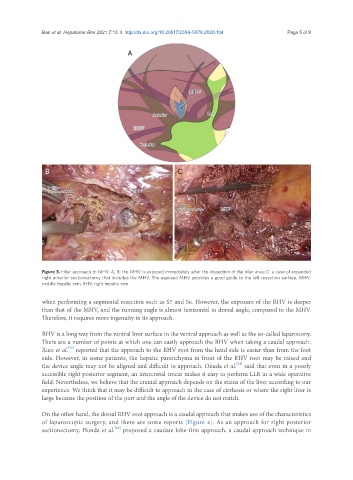
Figure 3. Hilar approach to MHV. A, B: the MHV is exposed immediately after the dissection of the hilar area; C: a case of expanded
right anterior sectionectomy that includes the MHV. The exposed MHV provides a good guide to the left resection surface. MHV:
middle hepatic vein; RHV: right hepatic vein
when performing a segmental resection such as S7 and S6. However, the exposure of the RHV is deeper
than that of the MHV, and the running angle is almost horizontal to dorsal angle, compared to the MHV.
Therefore, it requires more ingenuity in its approach.
RHV is a long way from the ventral liver surface in the ventral approach as well as the so-called laparotomy.
There are a number of points at which one can easily approach the RHV when taking a caudal approach.
[23]
Xiao et al. reported that the approach to the RHV root from the head side is easier than from the foot
side. However, in some patients, the hepatic parenchyma in front of the RHV root may be raised and
[24]
the device angle may not be aligned and difficult to approach. Okuda et al. said that even in a poorly
accessible right posterior segment, an intercostal trocar makes it easy to perform LLR in a wide operative
field. Nevertheless, we believe that the cranial approach depends on the status of the liver according to our
experience. We think that it may be difficult to approach in the case of cirrhosis or where the right liver is
large because the position of the port and the angle of the device do not match.
On the other hand, the dorsal RHV root approach is a caudal approach that makes use of the characteristics
of laparoscopic surgery, and there are some reports [Figure 4]. As an approach for right posterior
sectionectomy, Honda et al. proposed a caudate lobe-first approach, a caudal approach technique in
[10]