Page 95 - Read Online
P. 95
Page 6 of 17 Rastogi. Hepatoma Res 2020;6:47 I http://dx.doi.org/10.20517/2394-5079.2020.35
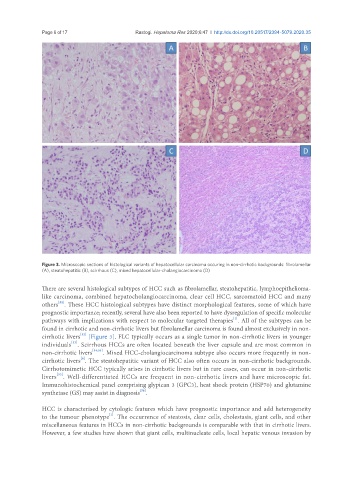
Figure 3. Microscopic sections of histological variants of hepatocellular carcinoma occuring in non-cirrhotic backgrounds: fibrolamellar
(A), steatohepatitic (B), scirrhous (C), mixed hepatocellular-cholangiocarcinoma (D)
There are several histological subtypes of HCC such as fibrolamellar, steatohepatitic, lymphoepithelioma-
like carcinoma, combined hepatocholangiocarcinoma, clear cell HCC, sarcomatoid HCC and many
[52]
others . These HCC histological subtypes have distinct morphological features, some of which have
prognostic importance; recently, several have also been reported to have dysregulation of specific molecular
[1]
pathways with implications with respect to molecular targeted therapies . All of the subtypes can be
found in cirrhotic and non-cirrhotic livers but fibrolamellar carcinoma is found almost exclusively in non-
[52]
cirrhotic livers [Figure 3]. FLC typically occurs as a single tumor in non-cirrhotic livers in younger
individuals . Scirrhous HCCs are often located beneath the liver capsule and are most common in
[53]
non-cirrhotic livers [54,55] . Mixed HCC-cholangiocarcinoma subtype also occurs more frequently in non-
cirrhotic livers . The steatohepatitic variant of HCC also often occurs in non-cirrhotic backgrounds.
[6]
Cirrhotomimetic HCC typically arises in cirrhotic livers but in rare cases, can occur in non-cirrhotic
[52]
livers . Well-differentiated HCCs are frequent in non-cirrhotic livers and have microscopic fat.
Immunohistochemical panel comprising glypican 3 (GPC3), heat shock protein (HSP70) and glutamine
synthetase (GS) may assist in diagnosis .
[56]
HCC is characterised by cytologic features which have prognostic importance and add heterogeneity
[1]
to the tumour phenotype . The occurrence of steatosis, clear cells, cholestasis, giant cells, and other
miscellaneous features in HCCs in non-cirrhotic backgrounds is comparable with that in cirrhotic livers.
However, a few studies have shown that giant cells, multinucleate cells, local hepatic venous invasion by